In our time, society does not attach due importance to physical education lessons at school. Someone thinks that at school there is nothing interesting and useful in physical education lessons and it is better for the child to do additional lessons, while someone is just lazy and he / she does not go to these lessons on principle. An even more frightening trend is the fact that the promotion of a lifestyle in which sport is assigned an important and fundamental role has practically disappeared in our country. That is why it is necessary to understand and realize what is the usefulness of physical education lessons at school.
Approximate standards from 1 to 11 grade
|
Exercises |
Boys | Girls | |||||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | ||
| Running 30 m (sec) | 6,1 | 6,9 | 7,0 | 6.6 | 7,4 | 7,5 | |
| "Shuttle run" 3x10 m (sec.) | 9.9 | 10.8 | 11,2 | 10.2 | 11,3 | 11,7 | |
| Skiing 1 km. | 8.30 | 9,00 | 9,30 | 9.00 | 9,30 | 10,0 | |
| Cross 1000 m. (Min., Sec.) | without time | without time | |||||
| Standing long jump (cm) | 140 | 115 | 100 | 130 | 110 | 90 | |
| Throwing medicine ball(cm) | 295 | 235 | 195 | 245 | 220 | 200 | |
| Throwing a small ball 150g (m) | 20 | 15 | 10 | 15 | 10 | 5 | |
| Throwing at a target from 6 m | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |
| Jumping rope for 1 min. | 40 | 30 | 15 | 50 | 30 | 20 | |
| Lifting the body in 1 min. | 30 | 26 | 18 | 18 | 15 | 13 | |
| Hanging pull-up (times) | 4 | 2 | 1 | ||||
| Pulling up in the hanging position (times) | 12 | 8 | 2 | ||||
| Seated forward bend (cm) | 9 | 3 | 1 | 12,5 | 6 | 2 | |
|
Exercises grade 2, approximate standards |
Boys |
|||||
| 4 × 9 m, sec | 12,0 | 12,8 | 13,2 | 12,4 | 12,8 | 13,2 |
| 3 × 10 m, sec | 9,1 | 10,0 | 10,4 | 9,7 | 10,7 | 11,2 |
| Run 30 m, s | 5,4 | 7,0 | 7,1 | 5,6 | 7,2 | 7,3 |
| Running 1,000 meters |
excluding time |
|||||
| Long jump from a place, cm | 165 | 125 | 110 | 155 | 125 | 100 |
| 80 | 75 | 70 | 70 | 65 | 60 | |
| 70 | 60 | 50 | 80 | 70 | 60 | |
| Pull-up on the bar | 4 | 2 | 1 | |||
| 23 | 21 | 19 | 28 | 26 | 24 | |
| Squats (number of times / min) | 40 | 38 | 36 | 38 | 36 | 34 |
| 12 | 10 | 8 | 12 | 10 | 8 | |
|
Exercises grade 3, approximate standards |
Boys |
|||||
| 3 × 10 m, sec | 8,8 | 9,9 | 10,2 | 9,3 | 10,3 | 10,8 |
| Run 30 m, s | 5,1 | 6,7 | 6,8 | 5,3 | 6,7 | 7,0 |
| Running 1,000 meters |
excluding time |
|||||
| Long jump from a place, cm | 160 | 130 | 120 | 160 | 135 | 110 |
| High jump method of stepping, cm | 85 | 80 | 75 | 75 | 70 | 65 |
| Jumping rope (number of times / min.) | 80 | 70 | 60 | 90 | 80 | 70 |
| Pull-up on the bar | 5 | 3 | 1 | |||
| Throwing tennis ball, m | 18 | 15 | 12 | 15 | 12 | 10 |
| Raising the torso from a supine position (number of times / min) | 25 | 23 | 21 | 30 | 28 | 26 |
| Squats (number of times / min) | 42 | 40 | 38 | 40 | 38 | 36 |
| 13 | 11 | 9 | 13 | 11 | 9 | |
| 6 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 1 | |
|
Exercises grade 4, approximate standards |
Boys |
|||||
| 3 × 10 m, sec | 8,6 | 9,5 | 9,9 | 9,1 | 10,0 | 10,4 |
| 5,0 | 6,5 | 6,6 | 5,2 | 6,5 | 6,6 | |
| Running 1,000 meters, min | 5,50 | 6,10 | 6,50 | 6,10 | 6,30 | 6,50 |
| Long jump from a place, cm | 185 | 140 | 130 | 170 | 140 | 120 |
| High jump method of stepping, cm | 90 | 85 | 80 | 80 | 75 | 70 |
| Jumping rope (number of times / min.) | 90 | 80 | 70 | 100 | 90 | 80 |
| Pull-up on the bar | 5 | 3 | 1 | |||
| Throwing a shadow ball, m | 21 | 18 | 15 | 18 | 15 | 12 |
| Raising the torso from a supine position (number of times / min) | 28 | 25 | 23 | 33 | 30 | 28 |
| Squats (number of times / min) | 44 | 42 | 40 | 42 | 40 | 38 |
| 15 | 14 | 13 | 14 | 13 | 12 | |
| Pistols, supported on one hand, on the right and left legs (number of times). (m) | 7 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 2 |
|
Exercises, grade 5 |
Boys | Girls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shuttle run 4 × 9 m, sec | 10,2 | 10,7 | 11,3 | 10,5 | 11,0 | 11,7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Run 30 m, s | 5,5 | 6,0 | 6,5 | 5,7 | 6,2 | 6,7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Run 60 m, s | 10,0 | 10,6 | 11,2 | 10,4 | 10,8 | 11,4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Run 300 m, min, s | 1,02 | 1,06 | 1,12 | 1,05 | 1,10 | 1,15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Running 1000 m, min, s | 4,30 | 4,50 | 5,20 | 4,50 | 5,10 | 5,40 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Run 2000 m |
Excluding time |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross 1.5 km, min, s | 8,50 | 9,30 | 10,0 | 9,00 | 9,40 | 10,30 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| from hanging, times | 7 | 5 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulling up on a low bar from a hanging position, times | 15 | 10 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Flexion and extension of the arms in the lying position | 17 | 12 | 7 | 12 | 8 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Raising the torso from a supine position, arms on the chest crosswise for 1 min, times | 39 | 33 | 27 | 28 | 23 | 20 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| , cm | 170 | 160 | 140 | 160 | 150 | 130 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Long jump with a run, cm | 340 | 300 | 260 | 300 | 260 | 220 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| High jump with a run, cm | 110 | 100 | 85 | 105 | 95 | 80 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-country skiing 1 km, min, sec | 6,30 | 7,00 | 7,40 | 7,00 | 7,30 | 8,10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-country skiing 2 km, min, sec |
Excluding time |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Skiing technique |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Many parents believe that physical education teachers at school are people who have nothing to do with sports or sports education. It is important to note right away that this statement is fundamentally wrong. First of all, you need to be aware that these days, not being a professional athlete in the past or a person who has sports education, it is almost impossible to get a job at school as a physical education teacher. This fact indicates that all those children who will engage in physical education at school under the supervision of a specialist practitioner or theorist (depending on the type of teacher's previous activity) will at least be able to achieve good results in certain sports disciplines, if they want to. It is very important that people attending physical education lessons develop in themselves motivational qualities. When compared in ordinary life, people who paid attention to sports and those who never wore sports suit, then the difference in life motivation is visible to the naked eye. People involved in physical education, and therefore most of those who attend physical education lessons at school, are much more successful, since even in school years in physical education lessons they develop such qualities as determination and overcoming themselves. According to statistics, those who do not attend physical education classes on a regular basis are twice as likely to get sick during flu epidemics than those who regularly attend physical education classes. As a consequence, those who are more likely to get sick have a large number of problems with academic performance, due to the fact that they attend fewer classes at school. It would seem that skipping school and unwillingness to attend physical education lessons at first glance are not connected in any way. However, if you trace the causal relationship described above, then it becomes clear why it is so important to go to physical education lessons and not look for excuses for yourself in order to once again sit on the bench, while classmates pass the standards or just play sport games.
Of course, it's hard enough to call modern school physical education perfect. And there are many reasons for this. But if you approach this lesson more carefully, consider what the teachers offer, do not try to evade and hide somewhere in the gateway, then in the future it will be possible to express many thanks to the teachers for this.
Now let's move away from loud phrases and try to figure out what is the real benefit of being in the gym, or on sports ground... First of all, it's about physiology. A growing young organism requires mobility in order to be able to disperse blood through the body. That is why children at recess and demolish ceilings in corridors or classrooms. And the more you try to keep them in the strictest discipline, the louder they will scream at recess.
Among other things, physical education sometimes allows a person to show hidden talents, which in a different environment he will simply hesitate to expose. After all, here, in fact, everyone is equal and everyone is on an equal footing, when few people will joke about your successes. But an experienced teacher will be able to assess the potential potential and develop it in the future. This is how future football players, volleyball players, basketball players, and athletes manifest themselves. After visiting the gym, many want to develop independently, improve their body and improve their health. And this is what is valuable in school physical education as a source of endless possibilities in the future. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
They are gaining popularity not only among professionals, but also among amateurs. These include powerlifting.
What's this?
To understand the meaning of powerlifting, it is enough to know that this word comes from the merger of two English words: "power" (strength, power) and "lifting" (lifting).
A bit of history
Back in the early 20th century, powerlifting emerged from the exercises that weightlifters added to their training. In the middle of the 20th century, competitions were already held in Western countries. From the beginning of the 60s, their rules were determined, after which powerlifting began to acquire modern features. 1964 can be considered the year of birth of this power species.
It was then that the first US Powerlifting Championships, albeit unofficial, took place. A year later, the athletes took part in the first national championship. 1972 was the year of the founding of the International Powerlifting Federation (IPF), and a year later the first world championship took place. In 1980, women competed for the first time at the World Championships, which took place in the United States; in 1989, the championships among and.
The World Powerlifting Congress (WPC) was formed in 1986, and later a large number of similar organizations appeared. Since then, powerlifting has become widespread in many countries of the world, it is loved not only by the stronger sex, but also by the beautiful part of humanity. 
Powerlifting today
Currently powerlifting is a complex that includes the following exercises:
- squats with a barbell on the back;
- bench press;
Due to the fact that there are three competitive exercises, there is another name - powerlifting.
All competing athletes are divided according to their weight into different categories, the number of approaches in each exercise is three. The overall result is the sum of the indicators for all exercises. Whoever lifted the most weight is the winner.  But this type of strength training is practiced not only for participation in competitions, but also for amateur purposes to improve strength indicators and strengthen the back, chest and legs.
But this type of strength training is practiced not only for participation in competitions, but also for amateur purposes to improve strength indicators and strengthen the back, chest and legs.
Did you know? In powerlifting, it doesn't matter how sculpted an athlete's body is, as opposed to. The most important factor in assessment-this is power. However, many bodybuilders started with powerlifting, such as Ronnie Coleman, Andrey Sorokin, and others.
Basic exercises
Let's take a closer look at the three types of basic exercises for powerlifting, taking into account the technique of their implementation.
Any exercise in powerlifting requires the correct positioning, because in the case of incorrect execution technique, you can seriously harm yourself. Therefore, when doing squats with a barbell on your back, you need to raise and focus your gaze forward at the selected point. Next, tighten the muscles of the upper back and tailbone.  Turn your knees outward and shift your weight to outer part feet. Remove the barbell from the rack and push it slightly wider than your shoulders. When performing a squat, first you should take your pelvis back and then bring your knees forward. In this case, the lower leg is straight, and the knees are gradually parted. This is the most secure position. Also, do not forget about the position of the barbell on your back.
Turn your knees outward and shift your weight to outer part feet. Remove the barbell from the rack and push it slightly wider than your shoulders. When performing a squat, first you should take your pelvis back and then bring your knees forward. In this case, the lower leg is straight, and the knees are gradually parted. This is the most secure position. Also, do not forget about the position of the barbell on your back.
Important! You should not place the bar too high, otherwise its weight will pull you forward, which is an incorrect and unsafe situation.
Of course, in order for it not to be difficult to hold, it is necessary to develop the flexibility and strength of the back muscles. There is one more note about this exercise, and that is the hand grip on the bar. It should be as minimal as possible to create tension in the back muscles used to position the bar. In addition, it is much more convenient to control movements in this position. However, you yourself can choose the optimal position of the hands for yourself, no one forces you to do so if you are uncomfortable. You can take a wider grip, but it is usually more difficult in this position to control the barbell on the back, and this is already done by advanced athletes. The same goes for the position of the legs when squatting. The wider you spread your legs, the more weight you can take. Therefore, beginners are advised to start with a leg position slightly larger than shoulder width.
The bench press is the second in the competition. Successful execution doubles the chances of winning.
Bench press in powerlifting is done in the "bridge", arching the back as much as possible. The fulcrum is the neck, shoulders and legs. The pelvis must be fixed in one position. Make sure that it does not come into contact with the bench. Keep your feet close to your shoulders to help stabilize your entire body and keep your muscles productive. The width of the legs is independently adjustable.  The barbell is gripped with your hands as conveniently, but keep in mind that the maximum allowable grip width in competition is 81 cm. Once you are ready to perform the bench press, you will need an assistant who delivers the bar. At competitions there are special assistants for this. Take a barbell without bending your elbows and slightly raising your pelvis. Place the barbell at chest level, bring your shoulder blades together and lower your shoulders. Place the basin back on the bench as well. Now you can lower the bar to your chest.
The barbell is gripped with your hands as conveniently, but keep in mind that the maximum allowable grip width in competition is 81 cm. Once you are ready to perform the bench press, you will need an assistant who delivers the bar. At competitions there are special assistants for this. Take a barbell without bending your elbows and slightly raising your pelvis. Place the barbell at chest level, bring your shoulder blades together and lower your shoulders. Place the basin back on the bench as well. Now you can lower the bar to your chest.
Important! The angle between the shoulders and the body when doing the bench press should always be 45° .
Then you need to perform the bench press itself, that is, raise the bar up on arms straightened at the elbows. It is necessary to ensure that the pelvis remains on the bench, without looking up from it. Do not move sharply, but slowly and smoothly.
- the final exercise in triathlon. Therefore, its implementation determines victory or defeat, but, of course, in the event that the athlete has successfully completed the two previous ones. Consider the sequential deadlift technique.
Before performing the thrust itself, you must take the starting position. There are two types of them: classic (legs shoulder-width apart) and sumo (legs wide apart). After the starting position is taken, you can lower the barbell down to about mid-calf level, while bending your knees. In the classic squat, the hands should be behind the knees, and in sumo, between them.
Important! The back when performing the deadlift must be flat, without bending. Otherwise, injury may result.
 Next, you need to lift the bar back and return to the starting position. This is due to the work of the muscles of the legs and back, the muscles of the arms are practically not involved during the lift. The center of gravity during the exercise must be shifted to. The pace of movements is similar to the pace of previous exercises - smooth and slow, without jerking.
Next, you need to lift the bar back and return to the starting position. This is due to the work of the muscles of the legs and back, the muscles of the arms are practically not involved during the lift. The center of gravity during the exercise must be shifted to. The pace of movements is similar to the pace of previous exercises - smooth and slow, without jerking. What you need for classes
When doing powerlifting, you can easily get some. When lifting heavy weight it is easy to overexert yourself and thereby damage some part of the body. Therefore, there are special devices for more safe execution.
Outfit and equipment
Powerlifting equipment can be supportive or non-supportive. Unsupported powerlifting is allowed to be used everywhere, taking into account "no-gear" and "outfit" powerlifting. There are such types of equipment:
 Within different federations(IPF, WPC, AWPC, IPA, IPA-A, WDFPF, GPC) T-shirts and overalls with 1-3 layers, as well as bandages of various lengths are allowed for equipment.
Within different federations(IPF, WPC, AWPC, IPA, IPA-A, WDFPF, GPC) T-shirts and overalls with 1-3 layers, as well as bandages of various lengths are allowed for equipment. Did you know? Equipment is used to protect against injury, as well as to take more weight... Thanks to bandages and belts, an athlete can lift 5-15 kg more, and now, with the advent of new modern products, the weight gain can be as much as 150 kg!
Now let's move on to equipment... It is represented by the following devices: 
Training rules
Powerlifting is primarily about strength. This means that the athlete should gradually increase the training intensity and the weight lifted. The lifter's training regimen is not the same as that of. If the bodybuilder works out one or more muscle groups, then the lifter - one or two competition exercises. Powerlifting training is very high intensity, so it is necessary to allow time for rest and recovery. You should also keep a pause of 2-5 minutes between sets.
The most optimal number of trips is 3-4 times a week. The very nature of the classes should be periodic. This means changing the load from light to heavy. It is best to make a weekly or monthly plan of different complexity and follow it.
As for nutrition, half of the lifter's diet should be complex carbohydrates, replenishing energy reserves. The simple carbohydrates found in baked goods and sweets will also be helpful for a quick post-workout recuperation.  Equally important in an athlete are. There should be enough of them for muscle mass to grow. This is approximately 35% of the diet. The remaining 15% is fat. They support and protect against damage. In addition to the training and nutrition regimen, one should not forget about the regimen. You need to sleep at least 8-10 hours a day, and also allocate time for daytime sleep if possible, because muscles grow during rest.
Equally important in an athlete are. There should be enough of them for muscle mass to grow. This is approximately 35% of the diet. The remaining 15% is fat. They support and protect against damage. In addition to the training and nutrition regimen, one should not forget about the regimen. You need to sleep at least 8-10 hours a day, and also allocate time for daytime sleep if possible, because muscles grow during rest.
Powerlifting guidelines for men and women
In every form, including powerlifting, there are standards. The standard in this case is total weight in kilograms when performing three exercises.
The presence of standards allows to divide athletes into weight categories and assign them sports titles. But there are certain peculiarities here.
The point is that there are many different organizations in this sport. This introduces some confusion with the regulations and not only.
In the IPF, which is the only one recognized by the International the Olympic Committee officially, and accredited by other government sports organizations installed such weight categories:
 And in alternative organizations, such as WPC / AWPC and others, the weight categories are different:
And in alternative organizations, such as WPC / AWPC and others, the weight categories are different: 
Also, the titles that are assigned to athletes differ.
According to the IPF, sports titles are awarded as follows:
- international master of sports - from 17 years old;
- master of sports - from the age of 16;
- sports categories in powerlifting, the same as in other sports - I, II, III and a candidate for master of sports - from the age of 10.
In other federations, the system of ranks and titles is very similar, but higher than the master of sports of international class in powerlifting, there is the title of "elite".
Consider the standards corresponding to different sports titles... It should be noted right away that the standards according to the IPF Federation are only for single-layer equipment, and in other federations there are also standards for multi-layer equipment and without equipment. For example, we will choose AWPC from alternative federations, which is quite widespread and opposed to the use of doping.
Single layer equipment
IPF Standards - Men, Women 

Layered equipment

Without equipment
 It should be noted that in many powerlifting organizations there are separate tables of standards for each of the exercises: for squats with a barbell, for a bench press, for a deadlift.
It should be noted that in many powerlifting organizations there are separate tables of standards for each of the exercises: for squats with a barbell, for a bench press, for a deadlift. Powerlifting Federation
The number of various powerlifting federations that take athletes under their wing is growing rapidly. There are organizations that are trying to develop uniform standards and are opposed to doping. And there are those who use athletes for wear and tear and consider their main goal to make a profit at any cost.
It is the presence of a large number of powerlifting federations around the world that calls into question the inclusion of this sport in the Olympic Games.
International
Among the federations international level only one has an official status, its representations are open in 108 states. This International Federation Powerlifting (International Powerlifting Federation).  Alternative powerlifting federations of international level:
Alternative powerlifting federations of international level:
- International Powerlifting Association (IPA);
- Revolution Powerlifting Syndicate (RPS);
- Xtreme Powerlifting Coalition (XPC);
- Global Powerlifting Committee (GPC);
- World Powerlifting Federation (WPF);
- World Drug-Free Powerlifting Federation (WDFPF);
- World Powerlifting Alliance (WPA);
- The World Powerlifting Congress (WPC), which includes the Amateur World Powerlifting Congress (AWPC), which conducts drug testing prior to competition;
- World Association of Bench Pressers and Deadlifters (WABDL);
- European Drug-Free Power Athletics Union.
Ukrainian
- National Powerlifting Federation of Ukraine, FPU (IPF), representative offices of the organization are located in Donetsk, Chernivtsi, Kharkov, Dnepropetrovsk, Poltava, Khmelnytsky regions;
- GP, All-Ukrainian Powerlifting Organization - IPA;
- UPC, Powerlifting Committee of Ukraine;
- Ukrainian Doping-Free Powerlifting Federation, UBFP - UDFPF;
- AWPC-WPC - Ukraine;
- GPA-GPF - Ukraine;
- RAW 100% - Ukraine;
Russian
- Russian Powerlifting Federation, FRP (IPF);
- OPR - Powerlifting Organization of Russia (representative of WPC / AWPC / GPC / WPF / WPA / WPU), holds competitions according to the version of a particular federation;
- ASM Vityaz - Power All-Around Association "Vityaz", founded in 2013, based on WPA-Russia;
- RDFPF;
- NAP - National Powerlifting Association;
- Union of Powerlifters of Russia (GPA / IPO representative);
- WRPF (World RAW Powerlifting Federation);
 If you decide to practice this sport, then good luck and brilliant in the competition!
If you decide to practice this sport, then good luck and brilliant in the competition! Content:
table bit standards barbell squat, no equipment (federations IPA, IPA-A)
standard, squat, squats with a barbell, table, without equipment, ipa, ipa-a
DISCHARGE STANDARDS FOR MEN (AMATEUR) | FEDERATION IPA-A
| Weight category (kilogram) | Elite | MSMK | MC | CCM | I | II | III | I (th) | II (th) | III (th) |
| 44 | - | - | - | - | 95 | 85 | 72.5 | 60 | 50 | 40 |
| 48 | - | - | - | - | 105 | 92.5 | 80 | 65 | 55 | 45 |
| 52 | 175 | 155 | 135 | 127.5 | 115 | 97.5 | 82.5 | 70 | 60 | 50 |
| 56 | 185 | 165 | 145 | 135 | 122.5 | 105 | 87.5 | 75 | 65 | 55 |
| 60 | 197.5 | 177.5 | 155 | 147.5 | 132.5 | 112.5 | 92.5 | 77.5 | 67.5 | 57.5 |
| 67.5 | 222.5 | 202.5 | 175 | 167.5 | 147.5 | 125 | 105 | 87.5 | 77.5 | 67.5 |
| 75 | 247.5 | 225 | 195 | 185 | 165 | 135 | 115 | 97.5 | 87.5 | 77.5 |
| 82.5 | 267.5 | 240 | 207.5 | 197.5 | 180 | 147.5 | 125 | 107.5 | 97.5 | 87.5 |
| 90 | 285 | 257.5 | 222.5 | 210 | 190 | 157.5 | 135 | 115 | 105 | 95 |
| 100 | 300 | 272.5 | 237.5 | 225 | 202.5 | 170 | 142.5 | 125 | 115 | 105 |
| 110 | 315 | 285 | 250 | 232.5 | 205 | 172.5 | 150 | 130 | 120 | 110 |
| 125 | 332.5 | 302.5 | 265 | 242.5 | 215 | 180 | 157.5 | 140 | 130 | 120 |
| 140 | 345 | 315 | 272.5 | 245 | 217.5 | 182.5 | 165 | 145 | 135 | 125 |
| 140+ | 352.5 | 320 | 277.5 | 247.5 | 220 | 185 | 167.5 | 150 | 140 | 130 |
BIT REGULATIONS FOR MEN (PRO) | IPA FEDERATION
| Weight category (kilogram) | Elite | MSMK | MC | CCM | I | II | III |
| 52 | 205 | 185 | 165 | 145 | 127.5 | 112.5 | 100 |
| 56 | 222.5 | 200 | 177.5 | 157.5 | 137.5 | 122.5 | 107.5 |
| 60 | 235 | 212.5 | 190 | 167.5 | 147.5 | 130 | 115 |
| 67.5 | 260 | 235 | 210 | 185 | 162.5 | 145 | 127.5 |
| 75 | 280 | 252.5 | 225 | 197.5 | 175 | 155 | 137.5 |
| 82.5 | 297.5 | 267.5 | 237.5 | 210 | 185 | 165 | 145 |
| 90 | 310 | 280 | 250 | 220 | 195 | 172.5 | 152.5 |
| 100 | 322.5 | 292.5 | 262.5 | 230 | 205 | 180 | 160 |
| 110 | 335 | 302.5 | 270 | 237.5 | 210 | 187.5 | 165 |
| 125 | 350 | 315 | 280 | 247.5 | 220 | 195 | 172.5 |
| 140 | 360 | 325 | 290 | 255 | 225 | 200 | 177.5 |
| 140+ | 365 | 332.5 | 297.5 | 262.5 | 232.5 | 205 | 180 |
DISCHARGE STANDARDS FOR WOMEN (AMATEUR) | FEDERATION IPA-A
(SITTING WITH BAR, WITHOUT EQUIPMENT, WITH DOPING CONTROL)
| Weight category (kilogram) | Elite | MSMK | MC | CCM | I | II | III | I (th) | II (th) | III (th) |
| 44 | 107.5 | 100 | 87.5 | 77.5 | 70 | 60 | 55 | 47.5 | 40 | 35 |
| 48 | 112.5 | 107.5 | 97.5 | 85 | 75 | 67.5 | 60 | 52.5 | 45 | 40 |
| 52 | 122.5 | 117.5 | 105 | 92.5 | 82.5 | 72.5 | 65 | 57.5 | 50 | 45 |
| 56 | 132.5 | 125 | 112.5 | 97.5 | 87.5 | 77.5 | 67.5 | 60 | 52.5 | 47.5 |
| 60 | 140 | 132.5 | 117.5 | 105 | 92.5 | 80 | 72.5 | 65 | 57.5 | 52.5 |
| 67.5 | 155 | 147.5 | 127.5 | 117.5 | 102.5 | 87.5 | 77.5 | 70 | 62.5 | 57.5 |
| 75 | 170 | 160 | 137.5 | 122.5 | 110 | 95 | 85 | 75 | 67.5 | 62.5 |
| 82.5 | 180 | 172.5 | 145 | 127.5 | 115 | 100 | 87.5 | 80 | 72.5 | 67.5 |
| 90 | 187.5 | 182.5 | 157.5 | 140 | 125 | 105 | 95 | 82.5 | 75 | 70 |
| 90+ | 195 | 185 | 162.5 | 150 | 135 | 110 | 97.5 | 87.5 | 80 | 75 |
DISCHARGE STANDARDS FOR WOMEN (PRO) | IPA FEDERATION
(SITTING WITH BAR, WITHOUT EQUIPMENT, WITHOUT DOPING CONTROL)
| Weight category (kilogram) | Elite | MSMK | MC | CCM | I | II | III |
| 44 | 140 | 115 | 102.5 | 90 | 80 | 72.5 | 62.5 |
| 48 | 155 | 127.5 | 112.5 | 100 | 87.5 | 77.5 | 70 |
| 52 | 167.5 | 137.5 | 122.5 | 107.5 | 95 | 85 | 75 |
| 56 | 175 | 145 | 130 | 115 | 102.5 | 90 | 80 |
| 60 | 187.5 | 155 | 137.5 | 120 | 107.5 | 95 | 85 |
| 67.5 | 202.5 | 167.5 | 150 | 130 | 117.5 | 102.5 | 90 |
| 75 | 215 | 177.5 | 157.5 | 140 | 122.5 | 110 | 97.5 |
| 82.5 | 225 | 185 | 165 | 145 | 130 | 115 | 100 |
| 90 | 232.5 | 192.5 | 172.5 | 150 | 132.5 | 117.5 | 105 |
| 90+ | 240 | 202.5 | 180 | 157.5 | 140 | 125 | 110 |
CONDITIONAL ABBREVIATIONS:
MSMK- international master of sports
MC- master of Sport
CCM- candidate to master sport
I- first rank
II- second category
III- third grade
I (th)- the first youth category
II (th)- second youth category
III (th)- third youth category
IPA- International Powerlifting Assosiation, National Powerlifting Association, no drug testing (no doping control)
IPA-A- International Powerlifting Assosiation, National Powerlifting Association, doping control works during the competition
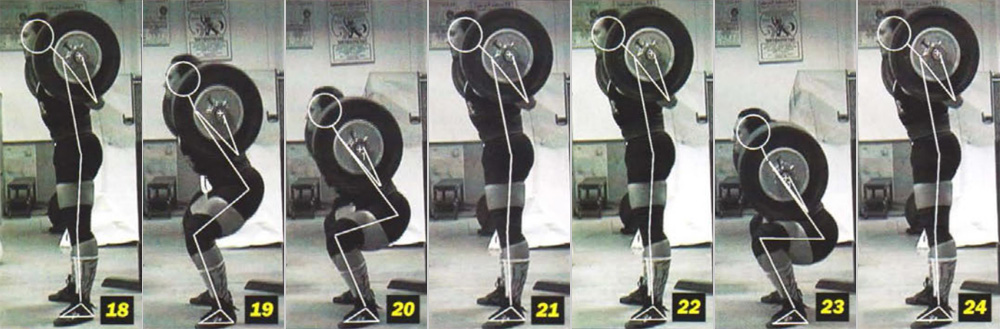
The rules for performing the exercise "Squat":
| 1. | After removing the bar from the racks, the athlete must take the starting position. The athlete should take an upright position with the barbell on his shoulders and place the barbell no lower than 6 centimeters from the top of the posterior bundle of deltoid muscles. The bar must be held horizontally, completely wrapping your fingers around the bar (position thumb not regulated). Legs should be motionless on the platform, knees should be straight. |
| 2. | In this position, the athlete must wait for the signal from the head referee. The signal is given after the barbell is correctly positioned on the shoulders and the athlete stops any movement. The head referee's signal shall consist of a downward movement of the hand and a loud “Squat” command. |
| 3. | The athlete should bend the knees and lower down until top part the surface of the legs at the hip joints will become no higher than the top of the knees. The knees should be fully extended both at the beginning and end of the movement. Only one sinking is allowed per attempt. |
| 4. | The athlete must independently, without double movement, return to an upright position with fully extended knees, motionless legs. The boom can stop, but it is not allowed to move downward. |
| 5. | When the lifter reaches a clear end position, the center judge gives the signal to return the barbell to the racks. The signal to return the bar to the racks consists of an upward and backward movement of the hand and a clear "Rack" command (to the racks). The athlete must return the barbell to the racks or make a visible attempt (one step to the racks), after which the athlete has the right to ask assistants to help him with this. If the athlete loses control and drops the barbell after the command "Rack" (on the racks), while making a visible attempt to return the barbell to the racks, then the attempt will not be counted and he is given an additional attempt. If an athlete deliberately throws the barbell, he will be removed from the competition. |
| 6. | The lifter must face the front of the platform. |
| 7. | During the exercise, no more than six and at least two assistants are allowed on the platform. |
| 8. | In case of an unsuccessful attempt to perform the exercise due to the fault of the assistants, the athlete receives an additional attempt to perform the exercise, which he has the right to refuse. |
| 9.1. | If the athlete was assigned a weight more than ordered, then: - in case of successful completion of this attempt, the weight to the athlete is counted; - in case of unsuccessful execution, the athlete is given an additional approach; |
| 9.2. | If the athlete was assigned a weight less than ordered, then: - if this attempt is successful, the athlete can either recognize the result of this attempt, or he may be given an additional attempt at the end of this approach; - in case of unsuccessful execution, the athlete is given an additional attempt at the end of this approach; |
| 10. | During the exercise, the athlete should not hold onto bushings, locks or discs. However, it is allowed to touch the inside of the rod bushing with the edge of your hand. |
| 11. | If the athlete drops the barbell on the platform during the squat, he will receive a warning, and the attempt will not be counted. When resetting again (at the same competition), the athlete is disqualified from this competition, and his result is considered zero. |
| 12. | World, European and Russian records can be set or surpassed at the world championship or national championships and any regional competitions, provided that all valid judges of the NAP (at least one of them are of the international category and the rest of the national ones) are present at these competitions, who must judge this attempt, as well as the presence of a sanction for fixing records. |
Reasons why an attempt to complete an exercise may not be credited:
| 1. | Failure to comply with the signals of the central referee on the platform. |
| 2. | Double standing or more than one attempt to get up from a squat position. |
| 3. | Incomplete extension of the knees at the end of the exercise. |
| 4. | An unsuccessful attempt to lower the torso to a position where the upper part of the surface of the legs at the hip joints is no higher than the top of the knees. |
| 5. | Assistants touching the bar between the referee's command "Squat" (to sit down) and the "Rack" command (on the racks). |
| 6. | Touching the elbows or forearms of the legs. |
| 7. | The impossibility of self-return of the bar to the racks. |
| 8. | Deliberately throwing the barbell onto the floor. |
| 9. | The athlete can use his own assistant in a position behind the athlete's back if required. |
How to squat a man with dumbbells on his shoulders, do a deep squat? How to squat right for a man: contraindications.
"Bodybuilders", "lifters", "turnstiles" - all these guys include squats in their workouts. Starting to regularly engage in any sport, squats should be given enough time, since it is important and necessary.
Performing an exercise with a barbell, kettlebell or sandbag - everyone decides for himself. In this article, we'll talk about the benefits of squats, how to build a squat session for 30 days.
The benefits of squats for men, squat standards
- For those who regularly visit the gym, it has long become an axiom that squats are an important part of the exercises that form prominent, strong legs and toned buttocks.
- In addition, squats are a kind of catalyst for the whole body. Simple exercises will help the athlete grow muscle mass. And if you have not yet discovered the secret of all the benefits of squats, allow yourself to skip these exercises in the gym, be sure to read the information below.
Why squats are useful:
- Squats are biomechanical work that builds muscle mass. In addition, the effectiveness of the strength properties of the muscles of the abdomen and lower extremities improves.
- We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the list, which contains the benefits of squats. The information will be useful not only for novice athletes, but also for those who spend a lot of time in the gym. This is not a call to action, but the motivation to do squats correctly so that you can enjoy your leg exercises in subsequent workouts.
- By doing squats regularly, you can increase muscle mass of the whole body. When doing squats, develop quadriceps, calves and hamstrings. The rest of the muscles are also engaged, and therefore, over time, you can see significant progress.
- Due to seemingly simple and monotonous exercises, the body is fed with anabolic steroids, the growth of muscle mass is stimulated. Testosterone and growth hormone are produced, which is why squats are an important part of the training program for those who dream of building muscle mass.
- By incorporating squats into your workout, you can significantly reduce body fat. This happens due to the growth of muscles, which burn fat. Stimulating muscle growth leads to the burning of large amounts of fat.
- If you do not skip workouts and build muscle on your skeleton, then during the workout, as well as during the recovery period, a lot of calories are burned. Therefore, if you are overweight, then you should not neglect squats.
- Previously, the word "squat" appeared in the vocabulary of athletes. Today there is another definition - "functionality". Until recently, squats were included in the training program of well-trained athletes and bodybuilders. Now this exercise is appreciated not only professional athletes... Squatting can be done in a variety of ways to prevent injury during exercise.

 If you are overweight, then you should not neglect squats.
If you are overweight, then you should not neglect squats. - Squatting maintains mobility. Increased strength and endurance are not the only virtues of the old good exercise called squats. They provide mobility for the whole body. Doing squats with full amplitude, on the other hand, promotes the development of all leg muscles. The feeling of fatigue in the legs will not occur, and therefore prolonged loads will become possible when performing exercises or during active recreation.
- Squatting improves coordination, a parameter that goes hand in hand with mobility and mobility. As a result, strength skills improve, muscle mass builds up, and a reserve is created for other exercises - the same squats, but on one leg, leg presses.
- The capabilities of the body as a result of doing squats increase: you will be able to jump further, you will run faster.
- The accessory muscles of the lower body, hips, and lower back develop, which reduces the risk of injury. Muscles work harmoniously, "with one command", the position of the body remains stable, therefore the risk of injury is minimal. However, it is necessary to observe correct technique squats.

 Increasing strength and endurance isn't the only benefit of the good old squat exercise.
Increasing strength and endurance isn't the only benefit of the good old squat exercise. Representatives of the stronger sex prefer this physical activity, which contributes to the acquisition of a beautiful muscle relief, elasticity of the hips. Why are squats useful for men?
- As a result of squatting, blood flow in the pelvic region increases, and the tone and elasticity of the skin improves.
- There is a study of the muscles of the press, back, which has a positive effect on posture.
- The heart and blood vessels receive a full cardio load.
- The muscles of the press are tightened, because the representatives of the stronger sex, who dream of a toned and embossed belly, should regularly perform these simple exercises.
- Reduces the risk of injury while performing power load... Knee, hip, ankle joints are being developed.
- You don't have to go to the gym, which has special equipment, to do squats. Exercises can be done anywhere and anytime.

 Why are squats useful for men?
Why are squats useful for men?
To keep the body fit and slender, a special squat program has been developed. It is designed for 30 days of regular classes. All exercises are performed under normal conditions, the presence of a special sports equipment not required. By doing squats according to the method described below, you can get rid of excess weight and body fat.
How to do it?
The result can be expected only if the technique of performing a set of exercises is observed. In addition, it does not cause difficulties even for novice athletes.
Squat rules:
- in the starting position, the back is flat and not rounded
- the abdominal muscles are tense, this helps to support the spinal column
- legs in the starting position are shoulder-width apart
- heels should fit snugly to the floor
- the feet do not come off the floor surface if during the exercise there is no straightening with lifting on toes
- At the lowest point, when performing squats, a right angle should form between the thigh and lower leg, the knees are parallel to the feet (if the knees deviate inward or outward, then the exercise is considered incorrect)
Benefits of the 30 Day Squat Program include:
- training of the gluteal muscles, quadriceps muscle and adductors of the thighs
- pumping the muscles of the whole body (oblique and rectus abdominal muscles, which form beautiful relief "squares")
- there is an increased impact on all groups muscle fibers lower limbs
- improves coordination and functioning of the joints
The 30 Day Squat Program is not monotonous. Exists different options performing a set of exercises that allow you to individually select the optimal load. You can perform squats with a barbell, with dumbbells. But these options are not for beginners. They'd better start with classical technique, and to enhance the effect, gradually connect sports equipment.
If it is necessary to increase the load, it is recommended to use weights, sports equipment.
Modification of the classic version of the set of exercises:
- Squats on one leg. This exercise is available for the advanced level. The difficulty lies in maintaining balance. To facilitate the exercise, you can stick to the support. The advantage of this exercise is that it involves more small muscles... During classic squats, they are not involved in the work.
- Doing squats using a weights. Any handy items, for example, bottles filled with sand, water, can perform the role of a load. If the complex is performed in sports hall, then dumbbells, a barbell, a bar from a barbell are used. The light weight of the weighting agent increases gradually.
- Plié on widely spaced legs in the starting position is performed with great depth.
Sumo exercise resembles a plie, with the only difference that the legs should not be very wide apart, and the knees and toes should be directed outward. - Doing shallow squats to work out other muscle groups.
- Squats against the wall. The exercise is performed in such a way that the back remains pressed against the wall. Squats are performed with the back sliding along the wall. Legs in the starting position shoulder-width apart. This exercise helps to relieve the back muscles and reduce the load on the spine.
Exhale squats instead of straightening. This exercise significantly increases the load. - With the steps to the side. Legs in starting position together. A step to the side is performed, and then inhale and squat. Exhale - initial position... Repeat the exercise in the opposite direction.

 Squat program for 30 days for men: description
Squat program for 30 days for men: description Additional load during squats can be provided by changing the position of the arms.
- Stretching your arms out in front of you help maintain balance.
- The hands on the belt provide a static load on the muscles that stabilize the body position.
- If you cross your arms over your shoulders, then those muscles that are responsible for stabilization are trained
If the hands are behind the head, then the load falls on the chest muscles, the respiratory and cardiovascular systems are trained.
For training to be effective, you need to do it intensively and regularly. And if you have not done it before, but decided to try out a set of exercises, then first determine your capabilities. Do not perform the entire complex or 100 repetitions at once during the first sessions. Start with a load that will invigorate your body and keep you energized.
The table shows the age norms and the number of squats for each level.
- The number of repetitions and repetitions is adjusted depending on the level of physical fitness. And if it is low, then in the first workouts there should be no more than 6-9 repetitions. At an average level, you can perform 12-17 repetitions.
- If you have high level training, then repetitions can be 20. Between approaches it is necessary to take a break, lasting 1 minute.
- You can start performing a set of exercises for a 30-day program only after the number of squats performed reaches 50.
30 day program workouts for the entry level:
| Workout day | Number of squats |
| 1 | 50 |
| 2 | 55 |
| 3 | 60 |
| 4 | Day of rest |
| 5 | 70 |
| 6 | 75 |
| 7 | 80 |
| 8 | Day of rest |
| 9 | 100 |
| 10 | 105 |
| 11 | 110 |
| 12 | Day of rest |
| 13 | 130 |
| 14 | 135 |
| 15 | 140 |
| 16 | Day of rest |
| 17 | 150 |
| 18 | 155 |
| 19 | 160 |
| 20 | Day of rest |
| 21 | 180 |
| 22 | 185 |
| 23 | 190 |
| 24 | Day of rest |
| 25 | 220 |
| 26 | 225 |
| 27 | 230 |
| 28 | Day of rest |
| 29 | 240 |
| 30 | 250 |
- Do not be intimidated by such numbers. At the beginning of training, it is allowed to perform squats in several approaches. Gradually, subject to regular exercise, the achieved result will only motivate you to increase the number of repetitions.
- According to reviews, the result of training will be noticeable after passing the equator of the program, namely on day 15. In order for different muscle groups to be involved in the work, the exercises must be performed in various modifications.
- For achievement maximum effect during training, it is necessary not only to correctly perform the exercises, but also to pay attention to your breathing. Squats refer to strength exercises with aerobic exercise.
- Compliance with the breathing technique improves endurance indicators.
- The most difficult areas during the exercise are overcome more easily if the inhales and exhales are performed correctly. In some cases from correct breathing depends on how many approaches the athlete can perform.
- Squats use muscle groups such as the buttocks, hips, and legs. When doing squats, a lot of energy is expended in the body. The exercise requires a certain amount of oxygen, otherwise it will be difficult for the body to cope with the task.
- This is not about the depth of breath, but about the timely inhalation and exhalation of air. The exhalation should be done with maximum effort.

 When doing squats, the mouth is only used for exhalation.
When doing squats, the mouth is only used for exhalation. How to breathe properly while squatting?
- Inhale and exhale through the nose.
- When working with large weights, exhalation is noisy. For beginners, a quiet exhalation method is recommended, without allowing the mouth to open wide.
- A deep breath is performed before squatting, after which, each time, inhale when reaching the top point.
- The exhalation is carried out at the moment when the maximum effort is applied, namely, at the lowest point, before the start of the pelvic lift.
- Do not inhale "in reserve", otherwise excess air in the lungs will cause rapid and shallow breathing. As a result, oxygen will flow unevenly to the tissues. In this case, even loss of consciousness is possible.
- To adapt respiratory system it is necessary to properly warm up before doing squats. This will help to ventilate the lungs as needed, improve blood circulation, and warm up the muscles.
How to squat men with a bar?
- Bodybuilding and powerlifting cannot be imagined without barbell squats. Thanks to simple exercise the muscles of the legs on the thighs develop, gluteal muscles... The barbell during squats increases the load on the muscles, which means the exercises become more effective.
- Barbell squats increase work different groups muscles. The result is an increase in muscle mass throughout the body.
To achieve the result, adhere to the following rules:
- The starting position during squats is with feet shoulder-width apart, toes pointing forward.
It is better not to tear the heels off the floor. - The hands on the bar are positioned symmetrically in relation to the center so as not to lose balance.
When doing exercises, the gaze is directed over the horizon line. Due to this position of the eyes, the athlete maintains correct position neck. - Lowering his eyes, the athlete involuntarily tilts his head, which can cause spinal injury or the appearance of osteochondrosis.
- The neck is located on the shoulders. You can keep sports equipment on the shoulder blades or on the anterior delta.
- Exercises are performed to a parallel position with the floor. You can go down below. In the first case, the load on the knee joint is less.
- Deep squats increase the effectiveness of the exercise.
- When moving up, push off the floor with your heels. After straightening your legs, take the starting position.
- Downward movement is accompanied by inhalation, upward movement - exhalation. You need to squat smoothly, not springing.
- Having reached the top position, keep your legs slightly bent.

 How to squat men with a barbell?
How to squat men with a barbell? How to squat men with dumbbells on their shoulders?
Video: Dumbbell Squats
How to squat men with a kettlebell?
Video: kettlebell squat
How to squat a man correctly so as not to injure his knees?
In the absence of knee injuries and correct execution exercise, you can not think about the risk of injuring your knees. However, you should still adhere to the following rules:
- The weight of the bar is selected based on the exercises being performed. Do not push the load and pace to the maximum.
Before you start exercising, take some time to warm up and rip your muscles. - Exercises are performed smoothly, without jerking. Sudden movements are not allowed.
- For maximum load on the legs and muscles, the squat is performed to a right angle.
How to squat right for a man: contraindications
You will learn how to do squats correctly by watching the video.
Video: Barbell Squats for Men | Technology and safety
Top 5 Common Squatting Mistakes for Men
Correct performance of squats:
- When removing the bar from the rack, bring the shoulder blades together. Squeeze the bar with your hands, accompanying with a deep breath and taking two steps back.
- Elbows "look" to the floor. The chin tilts towards the chest. Inhale again and perform a smooth squat.
- To avoid pain in your knees, move your hips back a little faster than your knees.
To perform deep squats, it is necessary to redistribute the load on the gluteal muscles and hamstrings. - A common mistake when doing exercises is shallow squatting. In the absence of leg injuries, the knee should be maintained at the correct squat depth. This means that the front of the thigh is below the top line of the patella.
Video: Squats. Male version
Recently, people began to say that barbell squats are unnecessary. Indeed, it is easier to tell a beginner that his lot is extension and flexion in the simulator, and some kind of leg press, than to explain the technical nuances of this basic exercise, systematically work on strength and flexibility, set the technique, monitor the body, work of the knees, legs, hips, do not allow the pelvis to "peck". In fact, the squat is available to everyone who has no contraindications for flexion in the knee, ankle and hip joints, and there are no contraindications for axial load on the spine. The movement is done in all sports, and there is plenty of room in fitness for a good technically correct squat, not just half-squats with a bodybar.

The load is evenly distributed between the long back muscles, quads, buttocks, hamstrings and calves. The muscles of the press, deltas, lats work as stabilizers. It is sometimes believed that the long back muscles also stabilize in the squat, but the actual situation depends on the technique. If the athlete is long-legged and his thigh is also long, the natural forward tilt of the back will be compensated for by work. long muscles back.
Benefits of Exercise

The main advantage for a fitness player is the ability to work out as many muscles as possible in a minimum of time. The truth is harsh - a person who does, for example, 4 working sets of squats of 8-10 repetitions with a relatively high weight, pumps the press and goes home or to work will be more difficult than his friend, who stays in the gym for an hour and a half, but performs only flexion and extension, and, at most, some kind of platform leg presses.
For athletes and advanced amateurs, squatting is good because:
- Builds overall lean body mass... The back also grows from squatting, it is not for nothing that experienced people will always identify the one who lies about their working weights on the Internet precisely by the look of his "pillars" (long back muscles);
- Enables more powerful footwork in all sports... MMA fighters and boxers, athletes and football players squat with a barbell. Yes, they don't lift the same weights as powerlifters, but they do this exercise to build power in the offseason. Plus, strength squats are key to injury prevention;
- Reshapes the thighs and buttocks... In bodybuilding " old school»No leg workouts for a healthy person without squats. Lunges and platform presses - auxiliary exercises, squat - main;
- Indicates overall strength... Although pure strength is mostly tested only in powerlifting competitions it is useful to know it. And exercises like the leg press are not indicators of strength, since the muscles of the body do not work in them;
- Improves health, including blood circulation in the pelvic organs, and increases bone strength;
- Increases energy consumption in training, helps to burn fat and build muscle
There are conflicting opinions about the benefits of squatting for beginners and fitness enthusiasts. Objectively, squatting with minimal weights improves coordination of movements, increases joint mobility and strengthens ligaments. It does not contribute to injury if performed smoothly and in a controlled manner. Opponents of squatting for beginners argue that the muscles of such people are too weak to support the weight on their backs and that the movement is technically correct. In fact, it makes sense to give a short period of "pumping" of muscles in the simulators before squatting, but it is not worth delaying it for 4-5 months, as some trainers do, so as not to put the beginners on the technique. The problem with beginners and amateurs is precisely the lack of skill and low joint mobility. The easiest way to do this is by squatting.

Beginners begin to learn the exercise by sitting on a box below the parallel of the femur to the floor. They perform a movement without a barbell, with a weight held at the chest, or with a bodybar on the shoulders. As soon as a person gets the skill of sitting with a flat back, without "untwisting" the lumbar spine at the lowest point of the exercise, and without a strong forward bend, he can begin to teach the classic squat with a barbell.
Before approaching even the minimum weight, you need to tune in and "scroll" in your head the sequence of actions. You do not need to run under the barbell as quickly as possible, and take it off at random, even if there is a queue for a projectile in the gym. Concentration in squatting is the key to avoiding injuries.

- The bar is installed at the height of the athlete's collarbone, or slightly lower. You need to come up, stand under the barbell in one movement and place it on the lower part of the trapezius muscle. In fitness it is best to avoid squats with the bar on the top of the trapezoid. They are quite traumatic for cervical the spine, and a novice athlete cannot always carefully remove and put the barbell from the racks, and therefore injures the neck;
- The grip should be slightly wider than the shoulders, but stable so that your hands do not slide to the pancakes. More than wide grips if the mobility of the shoulder joints is insufficient, but loss of balance must be avoided. The back should be tensely arched, that is, the shoulder blades are brought to the spine and lowered, but the press is tucked up and compensates for the natural lordosis. Throwing the tailbone upwards should not be done, if such a movement is obtained in a natural way, it is necessary to strain the front surfaces of the thighs and "tilt" the pelvis forward so that the pelvic bones begin to look straight ahead;
- The bar is level. The feet are under the bar in one line, the bar is projected to the middle of the arch of the foot, the knees are slightly bent. In one movement, the athlete extends both knees and raises the bar over the racks;
- Then you need to pull your belly inward to stabilize, make sure the bar is level, and follow the three steps - right foot back, with the left foot to the right, and the placement of the feet shoulder-width apart or slightly wider. The socks are turned to the sides, not forward. Do not squat with a barbell with parallel feet. If you need this particular squat option, it is better to fix the lower leg in special simulator and hold the burden in front of you;
- Next, the athlete makes sure that his back is slightly tilted forward, the shoulder blades are brought together and lowered, the press is pulled up, takes a breath, and begins to spread and bend his knees towards the toes. No pelvic movement is required. And even more so, they should not stretch back, sit on an imaginary chair, etc. There is enough energy from bending the knees and lower legs so that the hip joints can work in the nature conceived for them, and not the plane imagined by bodybuilders-beginners. On the contrary, while squatting, you need to monitor the "cranking" of the pelvis and back tilt. The first should be absent, and the second should be the minimum acceptable. In the "fold", that is, initially with a back inclination, only tall people with a long thigh, they have no other anatomical variant;
- You need to squat not to the parallel of the thigh with the floor, but until the pelvic bones go below the top of the kneecap. Contrary to popular belief that the parallel squat is safe for the knee, the peak load in the parallel technique falls on the anterior cruciate ligaments. If you sit a little lower, the load is evenly distributed between the hip, ankle and knee joints, and the ligaments will not suffer;
- Once reached, you need to powerfully push off with your legs and begin to unbend your knees and rise. Back movements in fitness on small and medium weights should not be performed. Likewise, a shift in the center of gravity in the socks should be avoided;
- You don't need to squat quickly. You should return the back to its original position and control the press before each repetition;
- When all the repetitions are completed, you need to go to the racks, and by bending both knees, return the bar to them.

- There is no need to remove and lower the barbell "into scissors", that is, in the lunge position. With a working weight, the athlete can swing forward or to the side and he will fall;
- Squatting with a low bar is allowed, but not the bar over the shoulder blades position. This is sometimes given to girls to "load the buttocks." Fans of loading the buttocks can, after squats, do any tilt with a barbell or gluteal bridge, but break shoulder joints for the sake of a ghostly shift of emphasis is not worth it. Moreover, for most people, an extremely low barbell means the same significant forward tilt of the body;
- The advice of illiterate amateurs about pulling the pelvis back and observing the depth below parallel are mutually exclusive. If a person takes something out there, he will sit down only due to the "pelvic peck", or in a position where the body lies on the hips. Therefore, you need to clearly define yourself. If there are no injuries that prevent squatting, it is worth squatting in depth, due to the movement of the knees and without pulling the pelvis back. If there are any, it is worth discussing with the trainer options for replacing the squat with another multi-joint movement for the lower body;
- Extending the knees by the socks while squatting is not dangerous, or rather, it is - necessary condition doseda for people with a long hip. It is dangerous to squat with your kneecaps straight forward with parallel feet. The socks should be unrolled as far as possible. hip joint, all other options are not acceptable;
- But the placement of the feet is wider than the anatomical width that the hip joint allows is dangerous too. This can cause injuries to the joint that is recovering for the longest time, and even stretching of the adductor muscles as an unpleasant addition;
- The width of the squat "for health" is easy to determine. The athlete is forced to make a high jump and land at a comfortable width. The position of the feet upon landing will determine the possible variant setting width. It is allowed to move the legs 2 - 3 cm outward or inward, but not "twist" them to the sides for the ghostly desire to pump up the buttocks. By the way, a wide squat, in addition to the buttocks, grows the adductor muscles of the thigh well, so lovers of large pelvis and thin legs will not get what they want here.
Warm-up is the most crucial moment. Just running and pedaling is the most useless way to warm up before squatting. Cardio is done for no more than 5 minutes, then a series of glute bridges with support on a bench, a series of lunges with the right and left legs, and several approaches of squats without weight are performed without burdening. Then - from the empty bar they rise to the working weight from approach to approach, increasing the weight. The step is individual.

Some exotic ways of selecting weights are not for squatting. This is not an exercise to perform "in refusal", at least until the person learns to control the position of his body in any state of fatigue. Reps are done from 3 to 12, sometimes more, this is due to the level of the athlete and the purpose of the training.
Otherwise, they follow the rules:
- The last 2 reps should be difficult, but for the purposes of health-improving physical education, "work" is not hellish forward bends of the back, knees brought inward, and hips up. This is a tangible resistance of the muscles to the load, that's all;
- You must always start with an empty bar, then move in steps from 5 to 10 kg, until the working weight;
- On different days, it is possible to perform with different weights, since recovery after training is not linear;
- With the achievement of the level of "squatting my weight" for women, and "squatting 1.5 of my weight" for men, periodization is required, that is, cycling of the lungs and hard training, even if you squat once a week
Injured athletes and people with hyperlordosis should be conscious of squat training. Many people should not do squats, at least not until full recovery is achieved.
The movement itself is not dangerous for the lower back and knees, and with weights no larger than one's own, it can be performed without inclinations, bandages, and a belt.
For the prevention of injuries, you need to monitor:
- Press work... The abdomen should not protrude forward and be relaxed. Pressing the press to the belt is performed only if the athlete does power squats, in fitness it should be avoided;
- The initial position of the pelvis... There is no need, as it were, to stretch the buttocks up, which we often see in photos from fitness magazines. It looks nice, but it is very traumatic for the lower back;
- Knee position... They move in the plane of the foot, towards the toes, and not inward;
- Ankle mobility... If the lower leg is "clogged" from walking in heels or trying to pump up the calf, it is worth rolling it with a roller and stretching it a little before squatting.

This should be the shortest section. The Upright Smith Machine is not designed for squatting. In it, you can still somehow do the press, lunges and vertical press, but not squat. Why? It's simple. When squatting, the bar moves in a straight line only for super-flexible athletes professional level... For most fitness enthusiasts, it "travels" in an elliptical trajectory, and that's okay. If you "forcefully" try to straighten the trajectory, the load on the hip joint increases. It is worth putting your feet a little wrong, and you can get injured.
Squatting in a smith "square", that is, in the "feet in front" position, is one of the most anatomically unnatural movements that overload the spine. It is contraindicated for scoliosis, hernias, protrusions and even simple pain in lumbar due to hypertonicity. It is performed in bodybuilding for the sake of shifting the load to the buttocks, but they do it either healthy people, or those who prioritize pumping the buttocks, rather than maintaining health.
The advantages of training in Smith are, perhaps, for bodybuilding at a high level:
- During training, the athlete can use the work "almost to failure", since he has the ability to put the bar on the stops at any point of the amplitude;
- In one approach, you can change the setting of the feet;
- The most is allowed different position bar on the back, including a very high
If a person cannot squat with a barbell according to the level of his physical fitness, he should do a goblet squat or squat with a handle. block trainer but not the movement in the Smith machine.

Many are afraid to "swing the hips", but since this issue is not decided by training, but by nutrition, fears can be left outside gym... Girls who eat "to lose weight" do not pump themselves up an impressive mass.
Here is an example of a squat workout "for weight loss", all exercises are performed for 12-15 repetitions, with a rest of strictly 45 seconds between sets:
- Bar squat
- Romanian Dumbbell Deadlift;
- Flexion for the biceps of the hip;
- Gluteal bridge;
- Extension of the hip in a crossover on the buttocks
Types of squats
These varieties are performed for a deeper study of the muscles, or the study weak points power movement in powerlifting.
"Sumo"

Sumo pull stance is imitated. Develops hips, buttocks, adductor hips.
Frontal

The bar is held on the chest, a clear dosed is required. The forward tilt of the body is excluded.
Zerchera

The bar is held in place by flexing the elbow at waist level. The movement serves to correct excessive forward bend in the classic barbell squat.
Gackenschmidt

The bar is taken with a straight grip behind the back. Some people think that this is the best way to work out the hamstrings and buttocks.

One of the "scissor" movements that corrects for imbalances in the legs, in fact, one leg stands slightly behind on the toe, and the athlete simply lowers into the squat from this position.

The athlete stands on the box, pulls forward or simply lowers the non-supporting leg and performs the movement first with one leg, then with the other. This is to correct the "strength difference" in the legs.

 If all of the above arguments are not convincing enough, then a little experiment should be done. The student needs to compare his health for two months. Let him not go to school for one month and sit on the bench. In another month, you must attend all physical education lessons and follow all the instructions of the teacher. Every day of these two days, it is necessary to leave an entry in a special diary, in which the student will leave his impressions about the state of health and the general state of the body. After two months have passed, re-read the diary and compare your entries. Surely the conclusions for many will be amazing, but what they can be found out by conducting this experiment.
If all of the above arguments are not convincing enough, then a little experiment should be done. The student needs to compare his health for two months. Let him not go to school for one month and sit on the bench. In another month, you must attend all physical education lessons and follow all the instructions of the teacher. Every day of these two days, it is necessary to leave an entry in a special diary, in which the student will leave his impressions about the state of health and the general state of the body. After two months have passed, re-read the diary and compare your entries. Surely the conclusions for many will be amazing, but what they can be found out by conducting this experiment. Physical education lessons are designed to balance this imbalance. Correctly constructed physical warm-up allows you to disperse excess energy throughout the body. In this case, there is no fatigue, as well as the risk of sprains or other types of injury. Moreover, thanks to active
Physical education lessons are designed to balance this imbalance. Correctly constructed physical warm-up allows you to disperse excess energy throughout the body. In this case, there is no fatigue, as well as the risk of sprains or other types of injury. Moreover, thanks to active 