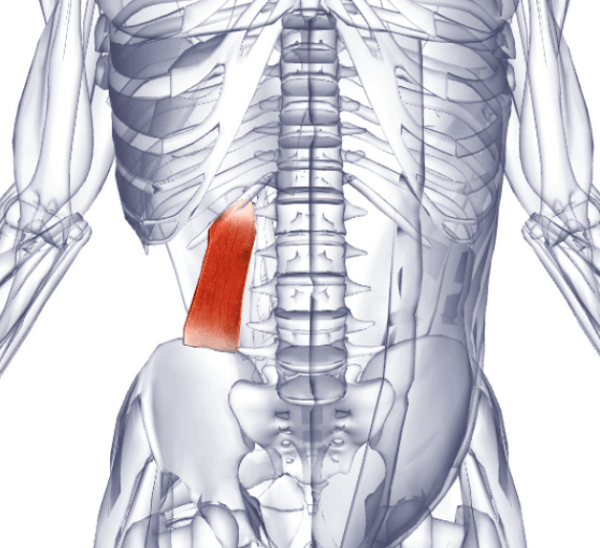
The square muscle of the lower back is a paired postural muscle that is responsible for lateral stability and tilt of the spine and chest, lifting the hip, and can also participate in the exhalation process. It begins at the iliac crest and is attached to the XII rib and the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae I-IV. Roughly speaking, it connects the lower ribs and the pelvis. This muscle is often the source of pain in the lower back. If gluteal muscles weakened, the square muscle of the lower back partially takes over their function of stabilizing the pelvis and, accordingly, is exposed to unintended overstrain. The site will tell you how to get rid of the pain caused by overexertion of the quadratus lumborum.
Overstrain of the square muscle of the lower back: the most common causes
The causes of back pain, namely in its lower part (lower back), can be:
- protrusion or hernia of the vertebral disc;
- trauma;
- pinched nerves;
- inflammation of the nerves;
- diseases internal organs(reflected pain);
- infections;
- rachiocampsis;
- spine diseases;
- difference in leg length;
- displacement of the joints;
- overexertion or muscle strain.
Suggest overvoltage square muscle the lower back is possible only after undergoing a complete examination and excluding other reasons that led to the appearance of pain.
A characteristic feature of problems with the square muscle of the lower back is painful sensation, as well as a noticeable tilt to the "painful" side. Possible causes of overstrain of the specified muscle:
- the habit of sleeping on one side with a raised hip;
- carrying weights on one side;
- weakened muscles of the buttocks;
- incorrect posture, etc.
How to relieve tension in the square muscle of the lower back
To relieve lower back pain, it is enough to perform the exercises below, aimed at relieving tension in the square muscle of the back.
Massage will also be useful, but it is better to contact a qualified specialist for it, who knows exactly the technique of performing massage movements.
We suggest you try the exercises and postures below.
1. We reach for the fruit (up to 10 repetitions)

- stand up straight, raising your straight arms up;
- now raise one hand higher as if you intend to pick a ripe fruit from the tree;
- bend the opposite leg at the knee and lift the hip up;
- inhale and feel the contraction of the square muscle of the lower back;
- exhale and relax;
- repeat on the other side.
2. Gentle twisting in the prone position

- lie on your side;
- apply a roller to the left thigh;
- turn the body in the direction of the roller;
- hands rest on the sides of the roller (as shown above);
- turn your head to any side (whichever is more convenient for you);
- You will have to look for the best position on your own, adjusting the bend of the hips and knees, pulling the thigh away from the lower ribs;
- linger in the chosen position for a couple of minutes;
- exhaling slowly, return to the starting position;
- repeat on the other side.
3. The graceful tree pose

- lie on your back;
- bend the spine so that the body tilts to the right side;
- keep your hips and shoulders on the floor;
- grasp your right wrist with your left hand;
- give your feet to the right;
- so that the legs do not part, it is fashionable to cross them in the ankle area;
- feel the entire left side stretch;
- after a few minutes, return to the starting position and repeat the pose on the other side.
4. Side stretch while sitting

- get down on all fours;
- place your hands exactly under your shoulders;
- knees and inner thighs should touch and be aligned under the pelvic bone;
- move your hips to left side rolling onto outer part left leg (right leg should be on the left);
- look over your right shoulder;
- inhale as you stretch the left lower back and left thigh;
- exhale to return to the center position;
- repeat on the other side.
5. Child's pose

- kneel down;
- sit with your buttocks on your heels;
- bend forward with your arms outstretched;
- put your chest on your hips;
- move your hands to the position of the arrow, which points to 10 o'clock, so that the body bends to the left;
- linger in this position for a minute;
- repeat on the other side (hands at 2 o'clock).
The site hopes that the above postures will help relieve tension in the square muscle of the lower back, and with it - and pain in the lower back.
Conditions modern life dictate their own rules to a person, under which a sedentary lifestyle becomes more and more common. As a consequence of this, a large number of people experience intermittent or persistent. Lumbar pains are the consequences of deformed, not correct posture, physically inactive lifestyle and many other factors. At the same time, pain in can cause not only discomfort, but also cause strong enough, literally unbearable suffering for the patient.
One of the main factors affecting the occurrence of lumbar pain. experts distinguish the syndrome of the square muscle of the lumbar trunk. It is located in the region of the spine and, like other muscles of the back, is responsible for maintaining it and moving it correctly. Injuries resulting from damage to this muscle will certainly lead to a decrease in the patient's motor functions and sometimes to quite severe pain in the state of mobility.
The square muscle of the lumbar spine is responsible for the stable functioning of the spine as a whole, and also participates in the tilting movements of the trunk. It has a paired structure and helps in raising the hips up, also takes a direct part in the breathing process, and more specifically, it contracts on exhalation. If, for example, a patient experiences coughing fits, then the square muscle undergoes numerous contractions, which leads to malfunctions in its work.

The location of the psoas square muscle begins from the twelfth rib of the spine. It is the link between the vertebral ribs and the bones of the pelvic region. It is this muscle, in most cases associated with lumbar pain, that acts as the source of the patient's unpleasant sensations. Often, the muscle in the lower back takes on a double function, performing the work of the gluteal muscle tissues, which, for one reason or another, cannot cope with the load. This can happen when the muscles in the buttocks are weakened or damaged. In this case, the square muscle takes care of the stable work of the pelvic spine, which often leads to its significant overstrain.
TO functional features square muscle include:
- bend along the axis of the spine to the left and to the right, while the muscle contraction occurs in accordance with the line of inclination of the back;
- fixing the body in an upright position. In this case, the psoas muscle experiences constant tension until the person takes a horizontal position;
- the lumbar muscle contracts on both sides when the body moves backward, as well as when it is returned from the forward position to the vertical position;
- participates in the process of excitation of nerve fibers located in the subcostal nerves and four lumbar structures;
- supplies blood to the aorta and subcostal arteries.
Groups of fibers of the square muscle of the lower back
Fibers of square muscles are divided into three groups in structure. The first of these is muscle tissue, the fibers of which are located vertically. It is located from top to bottom from the twelfth rib and extends to the pelvic part of the body. Thanks to these muscle fibers, the torso can be tilted forward and backward, as well as movements to the left or right. With this body movements to the left or to the right, they are accompanied by muscle tension on only one side, while the other side remains relaxed.

Under the second group muscle fibers understand the muscles located on the transverse processes of all lumbar vertebrae. In total, these processes are five in lumbar... These fibers of muscle tissue enter a state of tension when the torso is rotated in different directions. In this case, contracting, the muscle reduces the distance between the places of its attachments and there is a turn in one direction or another. In this movement, the oblique muscle tissue of the abdomen also takes part.
The third group of fibers originates from the horizontal processes of the vertebrae located in the lower back and continues up to the pelvic part of the body. This group of fibers allows simultaneous body movements in different directions.
As a result, it turns out that when turning the torso in the process of motor manipulations, two groups of fibers of the psoas muscle are involved. These turns often occur while walking. Moreover, they have symmetry in motion. However, if at least one of the three groups of fibers is damaged, shortened or simply weakened, then it will not be possible to make walking painless.
The greatest percentage of weakening of the square muscle occurs as a result of the displacement of the position of the twelfth rib spinal column... And also due to the change in location ilium... Often these processes are accompanied by modifications of the square muscle in the form of its shortening. In this case, there is muscle imbalance... The psoas muscle on the one hand turns out to be much shorter than the required length, and on the other, it becomes rather weakened. In this case, both sides of the muscle tissue begin to function unevenly, which leads to an unbalanced tone of this structure. With this violation, a number of negative consequences are revealed.
- An incorrect angle is formed when moving between the vertebrae located in the lumbar spine. This causes a change in the vector of motion of the vertebrae.
- When moving, the torso will have limitations, which leads to an asymmetry of the gait.
- An imbalance over time can lead to the appearance of intervertebral hernias - accordingly, the discs connecting the vertebrae will undergo destruction. As a result, the patient has the likelihood of acquiring arthrosis.
Therefore, in case of diseases of the muscles of the lumbar region, the first thing that needs to be restored is the square muscle. In this case, therapy should be aimed at the simultaneous restoration of both shortened and weakened muscles. The main thing is that all three groups of muscle fibers in the lower back receive appropriate treatment. Otherwise, the imbalance in the optimal work of movements will persist, and over time, the problem will again overtake the patient.
Causes of the weak state of the square muscle
The main reason for the shortening of the square muscle is the weakness of its paired part, on the opposite half of the lower back. This phenomenon is rooted in a person's irregular gait, in which both sides of the square muscles would have the maximum required tension. In this case, they speak of a shortened muscle in the lower back.
Opposite the square muscle in the frontal zone is the abdominal muscle, which is called the oblique. It is located opposite the square muscle, but in the abdominal area. For effective work right square muscle mass, the oblique muscle of the abdomen should simultaneously enter into tone with the lumbar counterpart. This contributes to the full stretch of the square muscle. Otherwise, the square muscle is shortened, which leads to an imbalance.

The second most popular cause of weakness in the quadratus lumbar region is the unhealthy condition of the gluteal muscle mass. Moreover, her weakness on the right side projects the weakness of the psoas muscle on the same side. This is because the lumbar square is trying to compensate for the weakness of the gluteus maximus. At the same time, it is overstrained and weakens over time. The consequences of such an overstrain of the lower back are its injuries in the process of constant movement in such a rhythm.
Pain points of the square muscle of the lower back
In order to find a focus of lower back pain, you must first determine the area of the square muscle. To do this, you need to find the twelfth rib: it lies below the entire rib row and is the shortest of them. Further, the horizontal processes of the vertebrae of the trunk and the ilium are found. This will be the localization of the square muscle, where these points are its boundaries.
When feeling the psoas muscle, the patient must be in a prone position. Examine the lumbar region by gently pressing in the area between the twelfth rib and the ilium. Palpation involves oblique movements towards the horizontal processes of the vertebrae. The greatest pain in the patient is caused by points located near the femur, starting with the ilium of the lumbar spine. Also, often strong pain localization can occur in the gluteal muscle tissue. Such pain can result in a loss of the ability to stand upright, walk, or roll over in a horizontal position (for example, turning to the other side while lying in bed). Square muscle pain can provoke a shortening of the lower limb, which can be noticeable with the naked eye.
Symptoms of diseases of the square muscle
Pain in the square muscle of the lumbar spine manifests itself in the form of a stressed state of the part of the back, located at the very bottom of the body. Patients with lumbar back pain often describe it as aching or severe, depending on the situation.
The patient also experiences discomfort in the lower back while lying down, but to a greater extent it begins to manifest itself or with any active body movements. Sharp pains usually occur due to coughing or sneezing, when a sharp spasm of the square muscle occurs. The position when a person is sitting is also no exception for the occurrence of pain of varying intensity.
The patient can experience these painful sensations systematically, and then they are called chronic. In this case, they are a huge problem for a person's ordinary life, since any active movement is accompanied by sharp discomfort, which leads to a decrease in the quality of life in everyday living conditions. In this case, over time, a person may even develop a deterioration in the psychological state due to the constant presence in uncomfortable conditions, accompanied by pain. Such people are more likely than others to be subject to depressive conditions and disturbances in the emotional background.

At the same time, experts noted that if a certain area of the body is exposed to constant pain, then another part of it takes over the work of this area. This is a natural natural defense of a person in order to maintain the functionality of the whole organism as a whole.
As for the square muscle of the lumbar spine, when it is painful, other muscle tissues take over the work to ensure the normal functioning of this area, which over time leads to their depletion and the formation of new destructive states.
In addition to the general symptoms described above, there are a number of other, more serious signs characterizing violations of the work of the square muscle of the lower back. They may indicate other diseases that directly provoked muscle dysfunction. These include:
- state of numbness of the lower extremities and feet;
- incessant pain even after rest;
- increased pain over time;
- dysfunction of the genitourinary system or gastrointestinal tract;
- a state of numbness in the perineum;
- stiffness of movements for more than half an hour after;
- subfebrile body temperature or increased sweating at night;
- significant reduction in body weight.
If the patient finds at least one of these symptoms in his condition, you should immediately contact medical professionals for a comprehensive examination and diagnosis.

Speaking about the consequences of overloading the square muscle, it should be emphasized that overstrain primarily leads to a change in the structure of the spine in the lumbar region. Here it is already advisable to talk about the deformation of the discs themselves, which are the connecting material of the vertebrae of the trunk. Therefore, it is extremely necessary to treat diseases of the square muscle in order to avoid the consequences in the form of deformity of the spine, the treatment of which implies more severe therapy.
Diagnostics of the syndrome of the square muscle of the lumbar spine
In medicine, a number of diseases are identified that can lead to deformation of the square muscle with all the resulting pain. It can be:
- trochanteritis or inflammation of the tendons of the hip joint;
- compression of the spinal roots;
- a decrease in the volume of intervertebral cracks;
- ankylosing spondylitis or fusion of intervertebral joints;
- arthritis and arthrosis;
- weakening of the muscle tissue of the abdomen;
- diverticulosis;
- endometriosis and pelvic inflammatory disease;
- fibroids or prolapse of the uterus;
- urinary tract infections.
The number of diseases that can lead to violations of the square muscle of the lower back is quite large. Therefore, for a highly effective diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out a whole range of procedures, which includes a blood test, research, etc. Experienced doctors with appropriate qualifications are able to identify the disease already during the palpation procedure. But it will be useful to conduct this series of studies in order to make a more accurate diagnosis.

Diseases of the square muscle of the lumbar region are widespread among people involved, for example, in summer cottages or vegetable gardens. These cases take place due to the systematic work of the trunk in a bent position, which increases the load on the lower back. In this case, the lower back can be susceptible to hypothermia due to frequent temperature changes by fresh air, what is the reason painful sensations... This is especially true for people with excess weight and pregnant women, in whom the load on the lower back increases significantly.
However, the most common square muscle syndrome is precisely in people leading a sedentary, sedentary lifestyle. This applies to office workers, people whose professions involve computers, and professional drivers. When they get sick, their blood circulation is impaired - it becomes slower. Accordingly, providing muscles nutrients decreases, and this leads to muscle tissue disorders in the lumbar region. It should also be emphasized that against the background of low mobility, tissues that are not involved in the processes of movement simply atrophy. In the case of the square muscle, which is directly responsible for flexion and extension of the trunk, the process of muscle atrophy will lead to its weakening and reduction in size. After the muscles of the lower back are weakened, the person will no longer be able to carry out the loads that were easily given to him at a young age. Accordingly, the activity of the whole organism as a whole will drop considerably, which will affect the quality of life as a whole. In this case, pain in the lumbar region may appear.

Lumbar Square Muscle Treatment
The patient often begins treatment of the lumbar spine only when the pain in the muscles begins to progress strongly. Of course, this is not entirely correct - it is necessary to start therapy at the first sign. Initially, therapy is directed to prevent the process of deterioration of the patient's condition. Further, the task of doctors is to improve the condition of the muscles of the back and the spine itself. And at the last, third stage, they are already engaged in reducing symptoms, that is, they are directly treating lower back pain.
But sometimes it becomes difficult to consistently carry out the stages of treatment. In this case, the pain is first relieved, and then they proceed directly to the treatment of the square muscle. Such a change in the order of the stages is possible, for example, in the inflammatory process of the soft tissues of the lumbar region. Here it will be advisable to first carry out drug therapy or massage procedures. In most cases, the initially prescribed drugs are antispasmodics, which help muscle tissue to relieve spasm and pain, because they interfere with a number of physiological procedures.

It occupies an important place in the therapy of the syndrome of the square muscle of the lower back. Unlike physical exercise, it does not carry a significant load on muscle tissue, and therefore is recommended at all stages of the disease.
However, do not forget that the main remedy in the treatment of back muscles is considered physical exercise as special exercises... After all, the appearance of problems with the lower back, namely its square muscle, is a consequence of a sedentary and physically similar lifestyle. Therefore, in order to return the lower back to its former physically strong state, it is necessary to remove the cause of the disease. To do this, it is necessary to achieve a return to active muscle work in order to make them more enduring and stronger. And this can only be achieved through physical exercise.
Methods
Depending on the stage of the quadrant lumbar syndrome, soft tissue repair measures can be prescribed, which often include a whole range of relief measures.
- Yoga combines a series of stretching and asanas. This helps to reduce pain in the psoas muscle. In this case, there is a beneficial effect of exercise not only on the physical, but also on the psychological state of the patient.

- Pain medications play a large role in relieving back discomfort, but they have a number of side effects... They can cause drowsiness, weakness, and dryness in the mouth.
- are designed to accurately administer pain relievers directly to the site of pain. If an inflammatory process is detected in the square muscle, then such injections may include steroid-based components. This type of therapy significantly relieves spasms in muscle fibers.
- Massage is beneficial for improving circulation and relaxing sore muscles.
- Ice can reduce inflammation in the back tissues.
- Heat increases blood flow to the sore spot and, accordingly, relieve pain.

Exercise to improve the condition of the square muscle
| Name | Exercise Description |
|---|---|
| Stretching | This exercise must be started by raising your arms up, while standing straight. Next, you need to raise one of the hands up as if a person is reaching for a tree for a fruit. In this case, the opposite leg must be brought into bent position relative to the knee and lift up. Then you need to relax the body, exhale and do the same with the opposite side of the body. Repeat the exercise ten times. |
| Twisting | Twisting occurs from a lying position on your side. At the same time, put a roller on the upper part of the left lower limb and raise the body, directing it in this direction. Stop for a short while in a tense position, and then, slowly exhaling, return to the starting point. Next, you need to roll over on the other side and do the same on the other side. Repeat 5 times on each side. |
| Stretching from a prone position | From a supine position, direct your spine to the right side, leaving your shoulders and pelvis on the floor. Next, grab with your left palm right hand and turn the foot to the right side. With this technique, the left side of the body should be significantly stretched. Hold this position for a couple of minutes, and then return to the starting point. Do the same on the left side to stretch the right side of your back. Repeat 5 times on each side. |
| Sitting stretches | The seated stretch comes from a point on all fours. In this case, the hands must be placed under the shoulders, and interior the thighs with the knees should be under the pelvis in the position where they touch. From this point, it is necessary to turn the hips to the left side, so that the right leg lies on the left. Lock in and look into the distance over your right shoulder. Inhale and exhale slowly without changing position. Return to the starting point and repeat the exercise on the other side. The exercise is performed 5-6 times on each side. |
| Stretching from a reclining position | It is necessary to kneel down, and then sit down so that the buttocks touch the feet. Next, you should stretch forward until the chest lies on the hips. Then with your hands parallel to the ground, show the time at ten o'clock, as if upper limbs- these are the hands of the dial. In this position, you need to linger for only a minute, and then turn your hands to the other side at the level of two hours. The exercise is performed 2-3 times. |
| Ponytail | This exercise is done from a standing position with your feet shoulder-width apart and your hands on your belt. We take a breath, while lifting the leg bent at the knee. Next, we exhale and take it away, taking a step back. We repeat the exercise seven times. We finish by returning to starting position... Relax and do the exercises in the same sequence for the other leg. |
| Extension for the side of the torso | The exercise is performed from a standing position, feet shoulder width apart. We make an upward movement with one hand, while the opposite hand lies on the lower back. With your free hand, we stretch upwards while inhaling, and while exhaling we move it towards the hand that lies on the waist. Then we change hands and repeat the movement in the other direction. The exercise is performed 8-10 times. |

Exercise stretching
- From a supine position, bend your knees and feet so that they are on the floor. Next, throw one leg over the other and lower it lower limb to the ground, with the upper leg on the healthy side of the body. Lock in for a few seconds. Repeat 5-9 times.
- Sit near the wall at a distance of about thirty centimeters and, without lifting your feet from the floor, turn your torso to the side. Turning around, put your palms on the wall and stand there for twenty seconds. Repeat 3-4 times.
- Remaining in a standing position, cross your legs so that the leg of the problem side of the back is in front and transfer your body weight to it. Raise your hands to head level, horizontally on the floor, and grasp the wrist of the opposite hand on the affected side of the body with one hand. Stretch your hand away from the problem side. Repeat 7-9 times.
- Stand straight - feet shoulder-width apart - and relax your arms by lowering them along your torso. Bend over to the healthy side so that the aching muscle on the opposite side is stretched to the highest degree. Inhale, while lifting your eyes up and fix this body position for ten seconds. Then lower your eyes down and exhale smoothly. Torso at this exercise should be directed strictly to the side. Repeat 4-5 times.
- Sit on the floor, fold over left leg and straighten the right one. Grab the right foot with a towel, and place the elbow of the right hand on the corresponding knee. Fix the pose, while inhaling and exhaling at least four times. Breathing during this exercise should be deep and smooth.
Measures for the prevention of diseases of the square muscle of the lower back
To prevent square muscle disease, you should learn how to correctly lift heavy masses so that the body remains level at the same time. In this case, weights should be held closer to the body. Also, experts do not recommend excessive physical activity or hypothermia to maintain the health of the back muscles.

For people leading a sedentary lifestyle, on the contrary, it is advised to give a load more often. lumbar muscles so that they do not weaken. It is necessary to regularly play sports or do specially designed sets of physical exercises. The main thing is that physical activity is regular and even. If there is no opportunity to fully engage in sports or physical exercise, it is necessary at least occasionally to take breaks in sedentary work and do a series of exercises that only take a couple of minutes of free time. This is easy to do, and the back muscles will receive the missing blood flow, which is the source of nutrition for muscle tissue.
The effect of the treatment of the square muscle can manifest itself at different intervals for each case. It all depends on the degree of the disease and the timely treatment of the disease. Nevertheless, the above methods of treating the square muscle give positive result In many cases.
Summing up
The square muscles of the lower back are responsible for most of the movements that a person makes in the lumbar region and the entire spine as a whole. Because this muscle is so "in demand", it can wear out faster - that is, pathologies may arise that affect it. That is why it is so important to get rid of them as quickly as possible in order to regain the ability to move freely.
Video - Trigger points in the square muscle of the lower back
Before starting your back workout, do warm-up exercises and warm up all the muscles in your body.
Let's start with the main basic exercises for square muscle of the lower back- exercises with axial load on the spine.
If you have back hernias or protrusions, take these exercises out of your workout. It is allowed to do it carefully with a minimum weight in statodynamics, in the absence of pain in the spine.
Strengthening the back or how to pump up the square muscle of the lower back
A healthy spine is the foundation of good and correct posture. But how do you strengthen your back muscles to avoid the so-called “square muscle syndrome”? In this article, we will talk about two training programs with and without axial load on the spine. By performing these exercises, you can not only strengthen your back, but also thoroughly pump up the square muscle of the lower back.
Exercises with axial load on the spine
Square Back Axial Load Complex
| Exercises | Sets | Reps / Time |
|---|---|---|
| Deadlift with a barbell | 4 | 15 |
| Dumbbell Deadlift | 4 | 15 |
| Barbell row on straight legs | 3 | 15 |
| Dumbbell Rows on Straight Legs | 3 | 15 |
| 3 | 15 | |
| "Good morning" sitting | 3 | 12 |
| 3 | 12 | |
| Dumbbell Wide Squats | 3 | 12 |
Deadlift with a barbell
Execution technique:
- Pick up a barbell.
- Bend your back straight. Place your feet parallel at a distance of 10-15 cm from each other.
- Lower the bar until it touches the floor, inhale.
- Raise the bar to the starting point by exhaling.
How many: 4 sets of 15 reps.
Advice. The exercise can be started from different starting positions when the bar is on the floor or when it is held in your hands. If the weight is heavy, lift the bar off the floor. If you are working with a low weight for the number of repetitions, do the starting position with the barbell in your hands.
Option - deadlift with dumbbells

It is performed similarly to the squatting exercise with dumbbells, the only difference is that the dumbbells are lowered in front of you, and not to the sides.
Exercise "Barbell Row on Straight Legs"

Execution technique:
- Hold the barbell in your hands.
- Place your legs with your feet parallel at a distance of 15 cm. Keep your back straight.
- Lower the bar as low as possible, try to keep the knees and back as straight as possible throughout the movement.
- Inhale and lift the bar back.
- Exhale as you climb.
How many: 3 sets of 15 reps.
Advice. Avoid arching in the back and strong bending of the knee joints.
Alternative: Straight Legged Dumbbell Rows

It is carried out in the same way as with a barbell.

Execution technique:
- Place the bar over your shoulders and hold with your hands.
- Stand shoulder-width apart. Bend your lower back.
- Lower the barbell down, bending in hip joints... Take your hips back and the body forward. Keep your back straight.
- When you feel the tension in the muscles of the back of the thigh, rise to the starting position.
How many: 3 sets of 15 reps.
Aimed exclusively at working out the square muscle of the lower back.

Square Back Sumo Barbell Row

Execution technique:
- Stand near the barbell on the floor with your feet wide, with your toes and knees turned to the sides.
- Hold the bar with your hands with a grip at a distance of 30-50 cm. Keep your back straight.
- Raise the bar at the expense of your hips and back as you exhale.
- Lock for one second and lower back down. Take a breath.
How many: 3-4 sets of 10 reps.
Option: Sumo Dumbbell Rows or Dumbbell Wide Squats

It is performed as with a barbell. Instead of a bar, hold the dumbbell in front of you.
Exercises to strengthen the square back muscle without axial load on the spine
Fulfill following exercises considered safe for people with back problems.
Complex without axial load for the square muscle of the lower back

Execution technique:
Starting position: Lie on the table with your stomach so that the pelvis protrudes beyond the base. Use a gym mat on top of the table. Hold on to the ends of the countertop. Legs are suspended.
- Raise your legs as high as possible while exhaling. The load can be adjusted by bending the knees. The more they are bent, the easier the exercise.
- Lower your legs. Breathe in the air.
How many: 3 sets of 10 reps.

Execution technique:
Starting position:
Find a level surface. For example, a sofa, bed or table. It would be a good idea to do the exercise with a partner who will hold your legs. If you don't have a partner, a heavy counterweight backpack will do.
Lie on your stomach on the bed so that the pelvis protrudes slightly forward. Put a counterweight on your feet or sit a partner. Hold the body horizontally to the floor, fold your arms in front of you.
- Bring your upper body down to the floor, exhale.
- As you exhale, rise to the starting position.
Number of repetitions: 3 sets of 12 reps.
Exercise "Boat" for the square muscle of the back

Execution technique:
- Lie on the floor with your stomach on a gym mat.
- Bend in the spine as much as possible, stretching your arms and legs upward. Keep your limbs straight.
- Hold for 2 seconds and lower yourself to the starting position.
Number of repetitions: 2 sets of 15 lifts.
Another exercise option
There is another option for performing the exercise. WITH alternating cross lifting arms and legs. Can be done by analogy with the previous boat.

"Plank" for the square muscle of the lower back

Execution technique:
- Stand on the floor, rest your elbows and toes. Keep your spine straight.
- Maintain this body position for 1 minute.
Perform 3 sets with 1 minute intervals in the plank and 1 minute rest.
13974 0
Proximal attachment. The medial half of the XII rib and the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae LI — L4.
Distal attachment. Upper-posterior region of the iliac crest.
Function. Unilateral action: tilts the spine to one side; pulls the XII edge down. Bilateral action: straightens the spine in the lumbar region; participates in forced exhalation, for example, when coughing.
Palpation. The square muscle of the lower back is very often the cause of the development of lumbar pain, but almost as often its role as a source of malaise is overlooked.
To localize the quadratus lumbar muscle, the following structures must be identified:
... The XII rib is the lowest and shortest of the ribs. Its free anterior edge is located posterior to the midclavicular line at the same level as the body of the L2 lumbar vertebra.
... Transverse processes of the vertebrae LI — L5.
... The iliac crest lies on the same horizontal line with the articulation of the L4-L5 vertebrae.
On palpation of the square muscle of the lower back, the patient should lie on his stomach. Palpate gently between the XII rib and iliac crest. Pressing should not be directed deep into the body, but obliquely and medially towards the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae. Imagine the location of the square muscle of the lower back, and your hand will find its lateral part.

Pain pattern. With a superficial location of trigger points, pain is felt along the lateral border of the iliac crest and up to the greater trochanter of the femur. Deep trigger points cause pain in the region of the sacroiliac joint and in the depths of the buttocks. Due to deep back pain, the patient may lose the ability to stand with the spine erect or walk. The pain can be caused by trying to turn on the other side in bed. Trigger points can cause visible shortening of the leg.
Causal or supportive factors.
Excessive load when lifting weights with the back bent at the lower back; prolonged and repetitive stress.
Satellite trigger points. Small and middle gluteus muscles, piriformis muscle and paravertebral muscles of the thoracic and lumbar regions.
Affected organ system. Genitourinary system.
Associated zones, meridians and points.
Dorsal zone. Foot meridian Bladder tai yang. BL 21-24, 51, 52.



Stretching exercises.
1. Lying on your back with bent knees and with your feet on the floor, swing the leg of the unaffected side to the other. With the "upper" foot, gently press the lower one, lowering it to the floor. Fix the pose until the count is 15-20.
2. Stand with your back to the wall, approximately 30 cm away from it. Without lifting your feet off the floor, turn your upper body and place your palms against the wall. Fix the pose until the count is 15-20.
3. In a standing position, cross your legs like this. so that the leg of the affected side is in front, transfer your body weight to it. Raise both hands in front of your head and grasp the affected side's wrist. Pull to the side to the unaffected side.
Strengthening exercise. Since the quadratus lumbar region is a postural muscle, strengthening exercises are generally not necessary.
D. Finando, C. Finando
The lumbar spine supports most of the body. Approximately 80% of adults experience lower back pain at some point in their lives. Sedentary muscle wasting is common, especially if you work in an office and lead a relatively sedentary lifestyle. To strengthen your lower back, start with a regular exercise program that consists of strength exercises, stretching and aerobics or exercise for of cardio-vascular system.
Steps
Do exercises to strengthen your back
-
Bridge with your hips. A hip bridge also helps strengthen the muscles in the lower back and core that support the spine, which leads to a reduced risk of lower back pain. For this exercise, lie on your back with your knees bent and your feet straightened on the floor in the same way as in the pelvic compressions.
- Raise your hips to the ceiling, keep your knees bent, and engage your core muscles. Stop when your hips are in line with your knees so you can draw a straight line (or bridge) from knees to shoulders.
- Hold the position for 5-10 seconds, breathing deeply, then lower yourself to the floor. Do 10 repetitions.
-
Do the Floor Float exercise. Also known as "Superman," this exercise involves lying facedown on the floor with your legs extended back and your arms in front above your head.
- If you are already lying on your back, roll over onto your stomach. Raise your arms above your head and extend your legs behind you.
- Raise your legs a few centimeters, and then swing alternately. You can also raise your left leg and right arm at the same time, then lower them and raise your right leg and left hand.
- Do 10 to 20 reps.
-
Contract your pelvic muscles. This exercise helps to strengthen the muscles at the base of the abdomen, as well as the muscles around the lower back. Learning to contract these muscles will help strengthen them so that you are less prone to lower back problems.
- To do this exercise, lie on your back with your knees bent and your feet flat on the floor. Your feet should be about hip-width apart.
- Press the arch of the lower back to the floor and hold for 5-10 seconds, breathing deeply, then lower yourself. Do 10 repetitions of this exercise.
-
Hunting dog pose. The hunting dog pose helps to stretch and strengthen the lower back and improve balance. When starting this exercise, get on all fours with your knees under your hips and your wrists under your shoulders.
- Extend your left arm forward and your right leg backward in a straight line from your fingertips to your heel. Keep your back straight, hold for two or three seconds, then return to the starting position and do the same with the other side.
- Do 10 to 20 repetitions of this exercise on each side. Keep your back straight and still, do not raise your head or heel above your back.
-
Add lunges. Lunges, if performed correctly, - great exercise to strengthen the lower back. Start by placing your feet about hip-width apart. Make sure you have a few tens of centimeters of space in front of you.
- Step forward with your right foot, lowering and bending your left knee. There should be a straight line from the top of the head to the left knee - do not lean forward towards right leg... Bend your left knee at a right angle so that the knee is straight over the ankle and the thigh is parallel to the floor.
- Hold the lunge for a few seconds, then return to the starting position and repeat with your left foot in front. Do 5 to 10 repetitions on each side.
-
Engage your core muscles while doing the plank. Since the muscles of the lower back are part abdominal muscles torso, you cannot strengthen the lower back without paying attention to the muscles of the core.
- Lie on your stomach and stretch your legs behind you. Stand up on your hands and toes so that there is a straight line from crown to toe.
- If you have not done the plank before, you can modify the exercise by doing it from your knees and elbows, or your toes and elbows, so that top part the body will rest on the forearms and not on the wrists.
- The lateral planks work with the lateral core muscles. Rise on your forearm, ankles on top of one another. Make sure your elbow is right under your shoulder.
-
Use a fitball to increase the difficulty. With a little practice, this exercise won't be that hard. Fitball adds an element of balance that makes the muscles work harder.
- For example, if you put your feet on a fitball to make a bridge, then both this exercise and holding the position will become much more difficult.
Stretch your lower back
-
"Cat-cow" for warming up. Exercise "cat-cow" is taken from yoga and involves changing the position from "cat" to "cow", at the same time, there is a synchronization of movements and breathing. Doing cat and cow regularly will make your spine more flexible.
- First, get on all fours with your back straight. Your wrists should be right under your shoulders and your knees under your hips.
- As you inhale, lower your belly to the floor and lift your ribcage and pelvis toward the ceiling so your back arches in a cow position.
- As you exhale, round your back towards the ceiling, picking up your tailbone and lowering your chin to chest... Repeat this cycle of inhalation-exhalation 10 to 20 times. Breathe in slowly and deeply, inhaling through your nose and exhaling through your mouth.
-
Boost blood flow with the Sphinx Pose. The Sphinx Pose helps increase blood flow to the lower back, which can help heal lower back problems and build muscle. First, lie on your stomach with your legs extended behind.
- Rise on your forearms, elbows just under your shoulders. Press your feet and palms into the floor, pressing your pubic bone until you feel the muscles in your lower back engage.
- Hold the position for 1-3 minutes, inhaling deeply through the nose and exhaling through the mouth.
-
Stretch the hamstrings, making the dog face down. Downward Dog is a classic yoga pose that stretches the entire body well and provides mental peace and improved concentration. Stretching the hamstrings, in particular, helps to strengthen the lower back.
- Get on all fours on a mat, knees strictly under your hips. The wrists can be flat under the shoulders or slightly in front. Concentrate on your breathing, inhaling slowly and deeply through your nose and exhaling through your mouth.
- As you exhale, lift your hips toward the ceiling, extending your arms in front of you until your body forms an inverted "V". The shoulders are rounded, the neck is relaxed.
- As you inhale, stretch your hips even higher towards the ceiling, shifting your weight from your wrists to your hands. On the next exhale, focus on your legs, reaching down towards your heels to stretch your hamstrings. Continue in this position for 10-20 inhalation-exhalation cycles, then lower yourself down to all fours again.
-
Twist your knees. Twisting the knees effectively stretches and strengthens your entire core and lower back, while the twisting movements move your spine and give it strength. First, lie on your back on a mat, straighten your legs.
- Extend your arms out to the sides of your shoulders so that your body forms a T on the floor. Then bend your knees to your chest.
- As you exhale, lower your knees to the right to the floor, your shoulders should be pressed against the karemat, that is, you twist from the lower back.
- Inhale and bring your legs back to the center, then on the next exhale, lower your knees to the left. Repeat 5-10 times on each side.
-
Lie in a baby's pose. Child's pose is a classic yoga pose at the end of classes, which also gives good stretch for the lower back. You can take this position from all fours - just lower your hips back and place your torso on your hips, arms outstretched in front of you.
- If you are flexible enough, you can rest your forehead on a pad. But do not bend over the line that is comfortable for you.
- You may find this position more comfortable if you move your knees slightly apart.
- Since the baby's pose is designed to be relaxed, you can lie down for as long as you like, breathing deeply.
Engage in aerobic exercise
-
Go for walks regularly. Walking is an easy, inexpensive way to get started. active life... Taking short walks for 15-20 minutes most days of the week will help strengthen both the lower back and the body as a whole.
- Try going out with a buddy to motivate yourself and make the walks more enjoyable. If you are walking alone, you can listen to music, a podcast, or an audiobook.
-
Ride your bike. If your lower back pain is so severe that sitting is easier than standing, cycling is a good cardiovascular workout option. An indoor exercise bike is a better option than riding bumpy, uneven terrain. If you have the opportunity to visit the pool and swim for 20-30 minutes, 2-3 days a week is great way strengthen the entire back. To avoid making any back problems worse, sign up for courses or hire a coach to improve your skills.
- Swimming is lightweight and the water is holding you back, making it a great activity if you have joint problems or are overweight.
- If swimming is new to you, start slowly with 10 minute swims. Every week or so, increase your time in the water by five minutes each time until you swim for half an hour each session.
- If swimming isn't your thing, walking or jogging in the water offers a certain amount of resistance, which helps strengthen your legs and lower back without having to worry about breathing.
-
Buy a pedometer. You should try to walk at least 10,000 steps throughout the day. A pedometer attached to your belt measures your steps, and some models also connect to the internet and have apps that let you track your progress over time.
- Choose an easy-to-use pedometer to help you reach your goals. You can purchase a very simple model or one that has many additional functions.
- If active image life is new to you, set yourself small goals first and work towards reaching 10,000 steps. Introduce walking breaks into your daily routine, such as park farther from the entrance when shopping, or walk up the stairs rather than using the elevator.
-
Maintain an active lifestyle. Sitting for long periods of time can lead to muscle atrophy in the lower back. Preventing this is simple - get up and walk every 30 minutes or so. If possible, try to reduce the total number of hours you spend sitting.
- For example, if you sit most of your work time, try standing up to do something when you get home instead of lying on the couch and watching TV.
- You can also purchase (or ask your boss to do so) a stand-up desk so that you can stand for a period of time during the workday.
Warnings
- If you already have low back pain, check with your healthcare provider before starting any exercise to strengthen your back. A physical therapist may prescribe specific exercises for you to reduce pain without causing any worsening damage or disease.
