Leads to a stroke, a sedentary lifestyle, excessive exercise. A person feels weak activity of the arm, hand, leg and fine motor skills of the fingers.
Why this happens: Due to the lack of physical movement, the blood circulates worse, preventing the brain from receiving the necessary energy. In the second case, there is a large release of adrenaline into the blood, which speeds up the work of the heart, enhances, and then disrupts the blood circulation in the brain.
Recovery complex of exercises for hands

It will take a long time to recover the original movements. Due to illness, a person may not feel his paralyzed parts of the body, and sometimes deny the presence of movement disorders, which can be encountered with low mental activity.
When doing the exercises, you must:
- Before starting the workout, you need to stretch the fingers of the paralyzed hand for about 15-20 seconds.
- Place the affected hand on the patient's chest, and in turn ask him to raise each finger. First, the exercise must be performed with the palm down, and only then with the arm extended.
- In exactly the same positions as in previous exercises, turn your fingers clockwise and counterclockwise. It is difficult to perform such gymnastics on your own, so a person who has suffered a stroke needs help.

- After the stroke, squeeze the patient's hand into a fist and then fully straighten the palm and spread the fingers.
- Close the left and right hands into the lock. In this position, the hands alternately raise and lower fingers.
- Alternate execution of clicks with the fingers of the paralyzed limb.
- Use a bumpy massage ball to warm up your fine motor skills.
To start moving the phalanges better, develop them with the help of a children's toy Rubik's cube. So the victim will quickly learn how to correctly control the gripping force.
The initial period of rehabilitation

To make it easier for the patient to restore the movement of the joints of the hand, he needs support. The warm-up at first should be aimed at restoring the large extensor and flexor muscles, and then knead the fine motor skills of the hands with the help of ergotherapy.
It is important in the exercises that the joints are involved, starting with the lightest, with a gradual transition to more complex exercises. If classes are difficult, offer to close your eyes and mentally imagine that a paralyzed hand and forearm work like a healthy limb.

If the development of fine motor skills is slow, praise the patient even for very little progress during recovery.
It is not worth doing all the difficult exercises for the patient, even if he also tries to help himself with his healthy hand at least to make it easier. It should be borne in mind that after a stroke, the restoration of arm movements always lasts longer; it will be much easier to rehabilitate a paralyzed leg.

If in a hospital rehabilitation after a stroke takes place under the supervision of experienced specialists, then at discharge, the patient is monitored by loved ones. It will only depend on them whether the victim will be able to stand on his paralyzed leg on his own or make movements with a brush or hand.
Rehabilitation is also important for the return of normal speech, memory and thinking. Blood pressure and cholesterol play an important role in recovery.
The main problem will come from the presence of spasticity in the arm and leg, which can be solved with the help of exercises aimed at the following:
- Decreased spasticity.
- Reducing the feeling of paralysis.
- Increased mobility of the arms and legs in the joints after a stroke.
- Improved tissue nutrition.

It is the spasticity that appears that interferes with any motor activity. This occurs as a result of prolonged immobility after a stroke.
To normalize tone and reduce spasticity during recovery, the attending physician may advise the victim's relatives the following:
- Constantly change the position of the injured arm and leg.
- Place a soft ottoman under the leg from the side of the spasticity at the level of the joint.
- At first, it is better to exercise under the control of others.
- Before starting the exercises, perform a warm-up aimed at stretching the paralyzed muscles.
- Monitor the room temperature with extreme care. Cold can trigger an increased feeling of spasticity.
- Warm up your hands during the massage, then proceed to the procedure. The movements of the masseur's hands should be soft with low intensity.
Rehabilitation speed

Each patient, in order to restore the basic movements after a stroke, needs to be engaged in an individual program.
How long it takes will depend on the following factors:
- During what stroke and side paralyzed leg or arm.
- How badly the brain tissue was damaged.
- The patient himself or with someone's help received medical treatment and how soon it happened.
- What methods and medicines were used during the rehabilitation period of the victim.
- Whether the patient took part in the conversation with the psychologist. How productive were the classes with the speech therapist and relatives. Whether this contributed to an improvement in the emotional state.
If the brain is not severely damaged, recovery may take 7 to 20 days. Under the worst circumstances, from six months to several years. One week or 2-3 months is enough for the development of speech abilities. To restore the movements of fine motor skills of the fingers, the hand must be practiced for at least 4 weeks. From one month to learn to lean on a paralyzed leg.

When the main rehabilitation process is over, but the patient does not perform some movements after a stroke quite correctly, then you can help if you involve him in simple home hobbies. For example, to interest you in beading, playing chess, checkers or cross-stitching.
If you have a computer at home, let it practice on the keyboard while typing. But especially important for the restoration of fine motor skills will be children's games such as a construction set with details: mosaics, pyramids or puzzles.

Try asking the victim to lift small items off the floor. A positive effect can be achieved if you ask to collect scattered small buttons, beads or small coins from the table.
Do not limit the victim to sports, only at the same time, monitor the intensity of the exercises performed. Crafts from colored paper or figurines will have a positive effect on restoring the mobility of the small joints of the hand. Useful sports for stroke patients are Scandinavian walking, light morning jogging without obstacles, cycling.
Spasticity. Part 1.
Earlier this word was unfamiliar to me. Spasticity resembles stiffness in severely frozen hands, when there is a desire to move fingers, but it does not work out. Plus, it also brings them down and crumbles.
When I started recovering from a stroke, this condition was almost throughout my entire body. It is especially strong on the left side. I was almost completely paralyzed, but I could still make small movements. They turned out as if in condensed milk. Tight, clumsy and very slow. There was constant tension in the hands, fingers. It did not go away for a minute, even in a calm state and did not allow normal movements. Hands involuntarily assumed an unnatural position. The left one was retracted by itself to the side of the body. The right one was bent at the elbow and pulled up to the chest. I was very tired physically and mentally from the fact that I could not relax. Only in the prone position was it easier. But as soon as he sat down, immediately the muscles of the body and limbs tensed as abnormal. Again, I quickly got tired of excessive stress. It turned out to sit for one or two minutes and the strength ended.
Spasticity made it impossible to make fine and precise movements. For example, if I was handed a cup of water, I couldn't take it. Didn't "hit" it, missed. When they put the cup in my hand, I could not hold it and wrap my fingers around it. They didn't shrink. At the same time, the tension in the hand was unreal. All this gimmick was wildly exhausting. To remove spasticity in all limbs at once is not a real task. Painfully, it is large-scale. And we, as always, have broken down a difficult task into simple fragments that have become feasible. We decided to divide the treatment of spasticity into pieces:
It has become easier. In the course of training, I noticed that the decrease in spasticity in the left hand was accompanied by a slight relief in the right and in the legs. The connection is not significant, but noticeable. We did exercises and massages evenly for the left and right limbs. Although the spasticity was much stronger on the left side of the body. Over time, everything became equal. This approach turned out to be correct.
It turned out to remove spasticity with a complex of gymnastics and massages.
Start with minimal movements.
Do not overload during exercise.
Do the minimum number of repetitions.
Do not do vigorous and vigorous massage. Only light touches.
Do not add or increase muscle tone.
Learn to relax muscles and release tension in them.
Do not do gymnastics to relieve fatigue spasticity.
Do it only in the morning.
While recovering from a stroke, I am used to the fact that there are no easy tasks. But removing the spasticity turned out to be an overly difficult job. The point is in the contradiction of the tasks performed. After a stroke, I needed to restore muscle strength throughout my body. That is, a lot of hard work. But at the same time it is necessary to treat spasticity. And for this, loads and endurance training are a hindrance. It turns out the first excludes the second. We solved this puzzle by alternating classes. One day: massage + gymnastics to relieve spasticity + exercises to restore balance and coordination. This does not require a lot of effort, the load is not great. The next day: strength training + endurance. And so in turn.
At the moment, the spasticity was removed. There are leftovers, but they don't get in the way. Freedom and lightness returned to movement. The tension is gone. Pain and muscle fatigue are gone. I began to spend less energy on movement. This made it possible to smoothly increase the load on morning exercises.
In order for recovery from a stroke to give good results, you have to follow such a regime. Gradually, I gain strength and increase stamina. Now I can conduct classes in one day. In the morning I do exercises with strength exercises. In the afternoon, gymnastics and massages to relieve spasticity + exercises for balance and coordination. Half a day, between classes, is enough for rest.
Treating spasticity after a stroke
Stroke is one of the most pressing problems of modern medicine. A high percentage of mortality and loss of performance, a tendency to form
persistent residual effects, frequent damage to patients of working age are the main points that explain the need to develop effective prevention and treatment measures.
Movement disorders are the most common consequence of all that are noted in patients after a stroke. The greatest chances of recovery are observed during the first months. Just during this period, many patients after a stroke develop muscle hypertonicity, which greatly complicates rehabilitation.
Development mechanism
To better understand the mechanism of development of muscle hypertonicity, let us consider the main aspects of movement regulation.

The earlier classes on prevention of spasticity begin, the better the result.
Muscle contractions are normally regulated at three levels:
- spinal cord;
- stem nuclei of the brain;
- cortex.
Any of these areas can stimulate muscle contraction. Thanks to the close cooperation of these departments, a person can perform the necessary movements, and muscle tone remains normal.
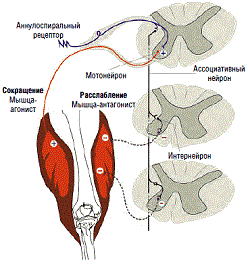
Impulses from motoneurons of the spinal cord provide automatic movements, for example, sharp bending when exposed to a painful stimulus. The overlying sections have a regulatory effect on the motor cells of the spinal cord, and it can be both inhibitory and stimulating.
The stem nuclei are responsible for maintaining posture and balance. The vestibular nucleus increases the tone of the muscles that extend the limbs. The red core, on the contrary, bends the limbs. In this case, the spinal motoneurons of the opposite muscle groups are inhibited. This relationship is called reciprocal.
The cerebral cortex regulates the voluntary movements of a person. To date, scientists have compiled detailed maps of the localization of areas that are responsible for the movement of individual parts of the body.
The motor cortex of the brain has an inhibitory effect on the spinal motoneurons, due to which integral movements are provided, and not individual twitching of the muscles. In a patient after a stroke, damaged areas of the cerebral cortex lose their inhibitory effect on the underlying structures. Outwardly, this is manifested by the development of muscle hypertonicity.
Treatment
Increased skeletal muscle tone is often a major barrier to recovery in stroke patients.
It should be borne in mind that the optimal result can be obtained only with a combination of drug and non-drug treatment methods.
Non-drug treatment of hypertension includes:
- correct positioning of the patient;
- massotherapy;
- gymnastics;
- physiotherapy procedures.

An integrated approach will help to overcome spasticity and restore motor functions of the limbs
Of the medicines, muscle relaxants and botulinum toxin are actively used.
Patient position
One of the main points in the treatment of muscle hypertonicity in patients after a stroke is giving the paretic limb a physiological position.

An effective way to deal with spasticity
The affected arm should be placed on a chair next to the patient's bed. Due to the increased muscle tone, it will be brought to the trunk. To prevent this phenomenon, a soft tissue roller is placed in the armpit.
The arm is extended at the elbow joint and turned with the palm up. To hold the limb in this position, sandbags or other devices are used. It is advisable to bandage the fingers and hand to the splint.
The leg should be slightly bent at the knee, and the foot should be at right angles to the lower leg.
The duration of the position treatment is about 2 hours. It can be repeated several times during the day. As soon as the attending physician permits, the patient is assisted to sit up and taught to walk.
Massage
Massage relieves increased muscle tone well. It must be carried out from the first days of the disease. From massage techniques it is necessary to choose stroking and light rubbing. They help to reduce muscle tone, improve blood circulation and lymph drainage in the paretic limb. The duration of the first sessions should not exceed 10 minutes. Over time, it is increased to 20 minutes. The duration of the course depends on the individual characteristics of the patient and is determined by the attending physician. As a rule, after 20-30 sessions a break of 10-15 days is required. After that, the course is repeated. The decision to discontinue massage therapy depends on the results achieved.
Physiotherapy
The complex of remedial gymnastics consists of active and passive movements. Passive movements consist of flexion and extension of the muscles, which is carried out by the caregiver. If possible, the patient makes passive movements with the help of a healthy limb. Due to the increased tone, the movements can be intermittent and abrupt at the beginning. Over time, the tone decreases, and they become smoother.

Exercise is very important for developing muscles and joints
As soon as the patient after a stroke is able to perform active movements, he should engage in therapeutic exercises on his own. In addition to flexion and extension exercises, exercises aimed at stretching the muscles are added. If done correctly, they relieve hypertonicity well and help the patient recover faster.
With increased muscle tone, the patient after a stroke is categorically not recommended exercises with an expander, an elastic band, and the like - they only intensify spastic phenomena and worsen the situation.
Muscle relaxants
Of the medicines for the treatment of hypertonicity in patients after a stroke, muscle relaxants of central action are used, which well relieve muscle tone without affecting their strength. Their mechanism of action is to inhibit pathological impulses that emanate from spinal motoneurons.
Treatment with muscle relaxants begins with minimal doses. If necessary, they are increased to achieve the effect. Expected effects:
- decreased muscle tone;
- improvement of motor functions;
- removal of pain syndrome;
- prevention of the development of contractures;
- increasing the effectiveness of medical gymnastics;
- facilitating patient care.
In our country, the most common muscle relaxants are baclofen, tizanidine, or sirdalud, tolperisone, or midocalm, diazepam.

Also, to restore and relax muscles, doctors prescribe muscle relaxants.
The lack of treatment with muscle relaxants is the possibility of developing side effects, of which the most common are:
- drowsiness;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- constipation;
- lowering blood pressure.
Botulinum toxin treatment
The use of botulinum toxin for the treatment of hypertonicity is indicated in patients after stroke with local spasticity.
The main indications for the use of botulinum toxin:
- lack of contractures;
- severe pain syndrome;
- violation of motor functions associated with increased muscle tone.
The mechanism of action is to block the transmission of impulses from the nerve cell to the muscle fiber. The clinical effect develops a few days after the injection and lasts for 2-6 months, depending on the individual characteristics of the patient. Due to the production of antibodies, repeated injections eliminate hypertonicity not so effectively.
This method is not widely used in the fight against hypertonicity in patients after a stroke. This is primarily due to the high cost of the drug.
Finally
Treatment of increased muscle tone in patients after a stroke is one of the key points that will not only significantly improve the patient's condition, but also make it easier to care for him.
Physiotherapy and massage are the main therapeutic areas, while monotherapy with muscle relaxants will not bring the expected result.
Medicines only enhance the effect of gymnastic procedures. This should be borne in mind by relatives or caregivers caring for the sick.
Post-stroke spasticity
Until now, we have hardly discussed movement disorders in our loved ones, since there is no direct connection with cognitive disorders here, and we did not want to blur the main theme of our website. However, recent discussion of the problems that develop after stroke - and in Russia, stroke remains a very common cause of dementia - has shown that this topic is important.
I was asked to tell about it without much ado, in simple words. I promised to try.
I read in a serious scientific journal that after a stroke, movement disorders are manifested in one way or another in more than 80% of patients. Due to the death of cells that previously regulated the work of muscles, they weaken (paresis) or turn off completely (paralysis). Disorder of body position and coordination of movements are also possible. This is fraught with falls and - at best - a developing fear of walking independently, and at worst - a fracture. The “head problems” that appear along with this only increase the risks.
Fortunately, even in old age, the plasticity of the brain allows it to rebuild and gradually restore the lost motor functions. And here the task of doctors (and after overcoming an acute disorder - and of those around them) is to create the necessary conditions for early rehabilitation: the main method is physiotherapy exercises in combination with physical and occupational therapy.
However, in about every third case, in the post-stroke period, the so-called spasticity begins to develop - an increased tone in the muscle, which prevents its stretching and forcibly returns the limb to a certain position, which limits overall mobility. The spasm is rather difficult to physiotherapy and interferes with normal recovery. As it turned out, visitors to our site also encountered such a phenomenon.
Due to the constant tone, which does not decrease even at rest, changes begin to occur in muscles, tendons and joints (fibrosis, atrophy), painful deformities (contractures) and pathological postures develop, which aggravate the problem and seriously complicate the patient's life.
Spasticity does not develop immediately, usually several months after a stroke. However, a specialist can notice the first signals in 2-3 weeks. Initially, flaccid muscles come to a tone, which increases and becomes more pronounced when responding to external stimuli (for example, an attempt to bend or straighten a limb). Six months later, maximum a year, spasticity turns into a problem that noticeably affects the patient's quality of life. It hurts.
In the upper torso, the shoulder, elbow, wrist, and fingers are often affected. In the lower body, spasticity can affect the hip, knee, ankle, or toes. The flexor muscles are usually affected in the arm area, and the extensors on the leg.
Look at the pictures from our newspaper "Memini". 

You've probably seen something similar in patients with cerebral palsy.
Needless to say, this problem badly affects a person's ability to dress independently, eat (simply not able to hold a spoon), write with a pen, hygiene suffers, etc.
If spasticity is not treated, then after 3-4 years contractures form - deformities of the joints. Bones are deformed too. Forced painful postures occur.
I will not write about who is to blame. Immediately I turn to the question "What to do?"
The answer is simple: heal.
Treatments for spasticity may include:
prescribing drugs (central and local action),
physiotherapy,
occupational therapy.
(In rare cases, a decision may be made about surgical treatment.)
The basis of therapy is the effect on the muscle, which allows you to reduce its tone. Below we will consider in more detail the role of each of these methods.
PURPOSE OF MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
Oral (taken by mouth) medications most commonly used to reduce spasticity include:
centrally acting muscle relaxants- baclofen, tizanidine, etc.
anticonvulsants- clonazepam, diazepam.
Both groups of drugs help to ease muscle contraction and improve range of motion. Their reception relieves painful muscle spasms, enhances the effect of physiotherapy exercises and, as a result, prevents the development of contractures. Unfortunately, the peculiarity of these drugs is that they act not only on the spastic muscles, but on the entire body as a whole. For the treatment of spasticity, these drugs are prescribed in high dosages, which leads to the appearance of side effects in the form of general weakness, dizziness, changes in mood and lethargy. This is especially unpleasant if the patient after a stroke and without it begins to develop cognitive impairment.
For this reason, more and more specialists are inclined to replace the above drugs with injections of botulinum toxin type A. In terms of the effect on muscle, botulinum toxin significantly exceeds all existing drugs taken in the form of tablets, and is comparable to surgical intervention. At the same time, denervation of the muscle with the help of a toxin is an extremely simple and safe procedure that can be performed by a doctor who has undergone appropriate training. Botulinum toxin preparations are well tolerated, and the likelihood of drug-drug interactions when using them is minimal. The recommendation of the American Academy of Neurology explicitly states the need to offer patients botulinum neurotoxin as one of the methods to reduce muscle tone and improve passive function in adult patients with spasticity.
In our country, three botulinum toxin preparations are widely used to treat spasticity: Botox (USA), Dysport (England), Xeomin (Germany). The latter is positioned by the manufacturer as a new generation drug, free from complexing proteins. In addition, the Chinese drug Lantox is registered in Russia, but, as far as I know, it is used mainly in cosmetology.
Physiotherapy has traditionally played an important role in the treatment of spasticity. The main components of the method include rehabilitation exercises, massage, acupuncture, thermal and electrical effects on spastic muscles, and the use of orthopedic devices.
Standard rehabilitation involves daily stretching to help restore strength to affected muscles, maintain range of motion in the joint, and prevent contractures. Regular stretching can ease muscle contraction and reduce stiffness for several hours.
Massage plays an important role in the restoration of motor functions and in the prevention of pathological conditions. It allows you to relieve pain, helps restore muscle performance, and improves their blood supply. However, only a specialist can be trusted to perform the massage, since spastic and hypotonic muscles need different influences.
In Russia, acupuncture is often used in complex therapy, but controlled studies conducted abroad do not show significant effectiveness of this treatment method.
Electrical stimulation is widely used to restore balance between flexor and extensor muscle tone. The effect usually lasts about 10 minutes when the stimulation is applied for the first time, but after several months of such procedures, the effect may be longer. Alternatively, the spastic muscle can also be stimulated directly to cause fatigue.
In the treatment of spasticity, limb-fixing bandages, bandages, tourniquets, splints, orthoses can be used. They allow you to maintain and align a spastic limb, as well as correct its deformity and improve function. Today, medical engineering has developed many orthopedic devices that provide not only immobilization and fixation in the correct position, but also deep pressure and maintenance of heat in the tissues. Modern devices include a setting mechanism that controls the desired function: from fixing with a lock to providing the necessary movement with assistance.
ERGOTHERAPY, OR LABOR THERAPY
Occupational therapy is a practice specially selected by a doctor that allows a patient to recover self-care skills after a stroke. Consider this as a special exercise in physical therapy, in which the exercise has a practical meaning: buttoning a button, using a cutlery ... Through occupational therapy - by repeating the same movements on a regular basis - patients recover lost everyday life skills whenever possible. Otherwise, when it is not possible to restore some important actions, occupational therapy makes it possible to choose adaptations that compensate for the loss of a useful skill, or to form new motor models, alternative to those used before the disease.
In other words, functional therapy is aimed at preserving all the functions of the limb through the restoration of old motor models and / or the creation of new dynamic stereotypes based on a new arrangement of muscles, which allows the normal execution of movements. An important role here is played not only by the patient's diligence, but also by the help of the person caring for him.
The two main categories of surgery for spasticity are performed at the level of the nervous system (neurosurgery) or bones, tendons, and muscles (orthopedic surgery). The most significant indication for surgical treatment is the development of contracture. In this case, orthopedic surgery is often the only treatment for spasticity. Through the operation, muscles can be denervated, tendons and muscles can be released from contractures, lengthened or moved, thereby reducing spasticity. Muscles can be denervated by cutting off specific nerves where they exit from the spinal cord (dorsal rhizotomy). This surgery is mainly used to treat severe spasticity of the leg muscles that interferes with the patient's movement.
To summarize briefly, the ideal option is to relax with botulinum toxin (lasts about 3-4 months) and develop. Here are just the prices.
Although I have read two studies. In one, the authors argued that if you calculate the costs that can be avoided thanks to botulinum therapy (nurse, aids), then in general it turns out even profitable. In another scientific language it is said approximately the following: it is better to spend money and get a result than to drink pills in large doses (by the way, they are also not free in our country), without much success.
True, both studies were carried out abroad.
Hand spasticity after a stroke
Mom has a stroke. Treatment and rehabilitation after a stroke.
2556. Ilya | 30.11.2013, 18:40:34
Please listen, everyone!
I myself am an instructor in the restoration of movements using wave techniques, and the author of the insult5.ru project.
2557. Ilya | 30.11.2013, 18:40:50
In addition, the muscles on the affected side are weak, atrophied, and it is not possible in principle to strengthen them with pills, injections, or massagers.
We have a technique, a training video, and the results, when a person is 68 years old, after a terrible hemorrhagic stroke and paralysis, after 5 months. exercises, the press shakes, and walks with light support.
Another of our wards (54 years old, with craniotomy, disorder of coordination of movement, could barely move, with severe spasticity of the arm and paralysis of the leg) within 3 weeks of classes began to get up himself without support, and stand straight (classes continue)
Another ward (72 years old, ischemic stroke 3 years ago, lack of any rehabilitation, contracture + paralysis of the left hand) for 2 lesson was able to move it to the fold, 10 cm, and raise it by 5 cm.
So, dear forum users! From my own experience, I want to say (I can no longer be silent, reading some comments) MOTION DISORDERS ARE TREATED IN THE MAIN WAY, CORRECTLY ORGANIZED, GENTLE MOTION, COMBINATION OF DYNAMIC AND WAVE LOAD. (And the fact that they grumble and sometimes make them nervous by their behavior - they are like children, they do not need pity, and they do not need punishment in the form of: "Oh, you are so! I will not come!" THEY WILL MAKE THEMSELVES: to the toilet, shave, eat, etc.
I do not want to be unfounded. And I suggest that those who really need help here, and not “just complain,” take a course of movement recovery at home. Go here: insult5.ru. I myself will guide you, advise you, send you the necessary exercises. And you will unsubscribe here on the forum about the results. This will help you, and will give hope to many others. I can personally help those in Moscow.
Articles
Exercises to restore movement in the hand
There are many literature sources and publications that describe exercises aimed at restoring hand function. However, most of the recommendations are suitable for people whose motor functions are not completely lost.
We will try to describe recovery process... starting with a complete lack of movement in the affected arm.
Hand exercises you need to start right away after paralysis. At the first stage, the main tasks of upper limb rehabilitation are:
1. Prevention of stiffness of the joints of the affected limb by performing passive movements in all joints of the paralyzed arm. Passive movements should be performed multiple times throughout the day.
2. Slowing down the process of muscle atrophy: if there are no contraindications, then massage and electromyostimulation are performed.
3. Prevention of injuries and stretching of the articular bag of the shoulder joint: when the patient takes an upright position, the sore arm should be placed in the shoulder bandage and fixed to the body.
1. Flexion - extension of the arm at the elbow.
2. The arm is bent at the elbow, straightening the arm up.
3. The arm is bent at the elbow, the shoulder is laid aside, the arm is extended upward.
6. Flexion - extension of the wrist joint.
7. Squeezing - unclenching the fingers.
8. Adduction - abduction and opposition of the thumb.
All exercises are performed passively (with outside help). The number of repetitions in each exercise is at least 50 times.
As active movements appear in the paralyzed hand, they begin to add active-passive exercises... which are performed with assistance or with the help of a healthy limb.
When active movements appear in the affected limb, special attention should be paid to the correctness of the restored movements.
As a rule, people, not knowing the intricacies of the recovery process, are happy with any movements that appear and begin to actively develop them - this is the main mistake... since in most cases, the first movements that appear are incorrect. Reinforcement of incorrect movements leads to the appearance of spasticity and the formation of spastic contractures and joint stiffness.
Examples of active-passive exercises in the supine position:
1. Flexion of the elbows.
2. The arms are bent at the elbows in front of the chest, straightening the arms up.
3. Raising straight arms up.
The exercises can be performed by keeping the fingers in the “lock” position or by fixing the affected limb (with an elastic bandage) to the gymnastic stick.
As the patient recovers, exercises begin to be performed from a sitting and standing position, which allows more amplitude movements.
Restoration of hand and finger movements
The most time consuming process is restoration of fine motor skills.
Many patients who have had a stroke, traumatic brain injury, and brain surgery develop spastic flexion contractures of the hand and fingers. Before starting to restore movements, you must remove pathological tone and develop contractures. Spasticity is relieved with the help of muscle relaxants, massage and physiotherapy procedures.
Development of contractures- the process is painful and traumatic: not every person is ready to endure significant pain. When the patient experiences pain, the tone in the affected arm increases, and therefore pain occurs when the joints develop.
This vicious circle allows you to overcome the correctly calculated scheme of rehabilitation measures... which includes:
Deep warming of spastic muscle groups and developed joints;
Electromyostimulation of antagonist muscles;
Passive development of joint movements;
Staged limb fixation in extreme positions using individual splints.
Let's take a closer look at these procedures.
1. Massage can be performed with the addition of warming ointments. The main task of the massage is to stimulate blood flow to the massaged area, warm up and give elasticity to the ligaments that are planned to be developed.
2. Deep warming up carried out with the help of physiotherapeutic paraffin and ozokerite applications. Prolonged exposure to heat reduces spasticity and promotes muscle relaxation. The development of the joint after warming up is less painful.
3. Electromyostimulation of antagonist muscles- This is the stimulation of muscle groups opposite to the muscles that are in spasticity. Thus, a balance is gradually formed between these muscle groups.
4. Passive joint development- gradual stretching of the spasmodic muscle, as well as the contracted ligaments. With the help of repetitively repeated passive movements, with a gradually increasing amplitude, the range of motion in the joint increases, the muscles and ligaments become more elastic.
5. After the development of the joint is completed, the hand and fingers must be fix in the extension position... to the maximum angle. Fixation can be done with wrist orthoses. as well as splints made of plaster or polymer bandage.
As the range of motion of the developed limb increases, the splints must be changed.
This scheme for the development of spastic contractures allows quickly achieve stable results... while causing a minimum of pain to the patient.
Recovery of hand and finger movements begins with active-passive exercises. After the movements of all fingers and movements in the wrist joint are restored, proceed to restoration of fine motor skills and finger movements separately: for example, learning to pick up and carry objects. The smaller the object, the more difficult it is to pick up and hold it.
An approximate set of exercises aimed at restoration of basic movements in the elbow, hand and fingers(exercises are performed while sitting at a table):
1. Flexion - extension of the arm at the elbow along the table surface.
2. Flexion of the arm at the elbow to the shoulder, without lifting the elbow from the table.
3. Sliding the hand on the table back and forth.
4. Circular movements of the hand on the table surface.
5. Turning the hand, palm up.
6. The brush hangs down from the table, lifting the brush.
7. Squeezing - unclenching of fingers, palm on the table surface.
8. Squeezing and unclenching fingers, hand palm up.
Muscle spasticity - what is it?
Muscle spasticity is a syndrome that develops with lesions of the areas of the upper motor neurons, while there is an increase in tonic reflexes as a result of stretching, combined with an increase in reflexes in the tendon area. The concept of muscle tone means a certain level of tension in muscle groups and the resistance that occurs during extensor or flexion movements of a limb segment. The normal condition is a feeling of some slight elasticity when palpating the muscles, as well as some muscle tension during unhurried movements. A certain increase in the tone of muscle groups is accompanied by strong resistance during passive movements.
An increase in muscle tone can greatly affect the regeneration of previously impaired functions. The high level of muscle spasticity does not allow the intact functions to be realized, as well as to fully recover the disturbed ones. At the same time, the increase in muscle tone is a compensatory factor in the development of paralysis. This determines the urgent need, immediately after the start of treatment, to clearly determine how necessary and useful it is to lower the muscle tone of the reduced arm or leg.
Spasticity symptoms
The main symptom of spasticity is involuntary muscle contraction. This process is accompanied by a headache and a general feeling of weakness throughout the body. Pain can not always be attributed to symptoms of spasticity. Very often, too abrupt movements become the cause of this condition, which become the cause of spasmodic contractions of the muscles of the arms or legs. In addition, pain can occur as a result of a change in the position of the patient's body, in particular at the moment when attempts are made to seat him.
The arms or legs, as a result of spastic contractions, stop obeying, become too weak, or acquire additional rigidity. In this case, a sick person with spastic muscle contractions may feel both weakness and some resistance from the muscles contracted by convulsions. These factors are a consequence of the conduction of muscles and nerves. In the case of taking medications, there is some relief of tense muscles, but a feeling of weakness remains.
Other symptoms of spasticity include involuntary contractions of individual muscle groups, as well as a feeling of general fatigue and loss of a sense of dexterity in the muscles. Numerous patient testimonies characterize spasticity as excessive muscle tension, weakness in the legs, and resistance to movements of the legs and arms.
Spasticity after a stroke
Stroke is an extremely important medical and social problem, since it is one of the causes of many cases of disability, usually related to impairments of human motor activity. In the overwhelming majority of all cases, the acute period of stroke is characterized by the detection of hemiparesis; in about two-thirds of all cases, there is a residual effect after a stroke. In the bulk of cases, stroke is observed in people of retirement age, and women are susceptible to it 20% less than men.
Immediately after the onset of a stroke, there is a decrease in muscle tone in the limbs, but after three days it recovers, eventually reaching the average. Depending on the severity of the stroke, the duration of the painful condition and the degree of muscle spasticity can vary. The basis of spasticity after a stroke is a violation of the activity of the parts of the human cerebral cortex responsible for the motor activity of the limbs.
Spasticity with cerebral palsy
The spastic form of infantile cerebral palsy is very common. Separately taken muscles of the child's body are at the same time in an increased tone, which occurs due to failures in the full functioning of the muscles of the arms and legs. The state of extreme tension is very typical for muscles with cerebral palsy and this is the reason for a strong slowdown in their growth. At the same time, there is a significantly faster growth of bones than muscles, which causes a significant difference in muscle length compared to bones and tendons. In this case, a decrease in the size of the affected limb occurs and the joints of this limb become less mobile.
In order to prevent all this from happening, immediately after the child is diagnosed with cerebral palsy, classes should be held with him. You can start with regular exercises using physical therapy exercises, the results of which will determine the methods of dealing with spasticity. This approach will contribute to the achievement of the desired results.
Spasticity in multiple sclerosis
Spasticity is a symptom that is most closely related to multiple sclerosis. However, when describing the symptoms of their condition, patients do not always interpret it correctly. Often they understand a spasm as a sharp wave of surging pain, while a spasm is an involuntary contraction of muscle groups. To avoid confusion, the meaning of these terms should be understood.
Spasticity in people with multiple sclerosis often manifests itself in the form of unexpected contractions of certain muscles. These contractions can arise by themselves, or they can be a reaction of the body to external stimuli. The degree of manifestation of such symptoms is very diverse, from a mild form to severe spasms that last for a long time. In this case, the patient will need to move in a wheelchair. With multiple sclerosis, spasticity may change over time. In this case, the muscles of the arms, legs are mainly involved, much less often the muscles of the back or other parts of the body.
There are some cases in which spasmodic muscle contractions may even be beneficial. This refers to conditions in which the sick person is too weak in the legs and the spasm helps him to take a stable position. In this case, when the spasticity is removed, the person's legs give way and he will not be able to stand on his own.
Spasticity treatment
Methods for treating spasticity can be different, some of them can be distinguished:
- physiotherapy is used to stretch muscle groups and maintain joint mobility, while reducing the risk of joint damage. With low muscle mobility, physiotherapy can be used as a means of gradually and smoothly stretching them. In some cases, it may be advisable to undergo minor surgery in order to increase the length of the ligament by making an incision in the leg;
- drug therapy is used in cases where it is necessary to take medications to relieve increased tension in the muscles of the legs. The mechanism of action can be different, some agents have an effect on the spinal cord, others on the receptors of the brain;
- Botulinum toxin is an agent that provides the proper effect when used to relax the spastic muscle for a short time. Ethanol or phenol can be considered an alternative, given that these drugs are suitable for short-term innervation of large and strong muscles, while pain in certain nerves may occur.
Exercise for spasticity
Spasticity manifests itself as a violation of motor activity, manifested in partial or complete immobility, increased muscle tone, as well as involuntary movements. There are certain exercises that can reduce spasticity, restore motor activity and eliminate synkinesis in paralyzed limbs.
Performing the exercises requires a certain synchronicity, and both affected limbs participate in them, move in the same direction at different or the same speed. You can do the exercises yourself, while you can use someone else's help. Execution implies a medium and slow pace, the number of repetitions is limited to four. You can rest by placing your arm or leg in a position that relaxes your muscles most effectively.
Massage for spasticity
In case of spasticity, the following massage methods can be used. The arms are connected on the chest, while the legs are pulled up to the abdomen, the body bends slightly at the same time, and in this position, free light swaying can be carried out, providing a decrease in muscle tone after a certain time. The time during which a decrease in muscle tone occurs should be used in order to conduct a qualitative stimulation of the restoration of certain motor functions that were impaired as a result of muscle spasm. If the muscle tone increases, it is recommended to repeat the described massage method. This technique is most effective when applied to children aged one month to seven years.
You can apply a form of massage, which is the normalization of muscle tone using a ball. To do this, you need to lie down on the ball with your chest and stomach, then make a series of movements in different planes, then change the position of the body and lie down on the ball with your back, subsequently repeating the entire set of movements listed above. Depending on the muscle tone at the time of the exercise, the duration of the exercise should be determined. On average, in total, such a massage method takes no more than fifteen minutes a day.
Folk remedies
With spasticity of the lower extremities, the following traditional medicine is recommended for use. According to the shape of the legs and the area of the body to the lumbar spine, it is required to sew bags, which are subsequently stuffed with birch leaves torn from a tree. Immediately before going to bed, the patient should be placed with his feet in these bags, and held in them for some time, while it is necessary to ensure that the leaves fit the human body as tightly as possible with a dense layer on all sides. This is necessary to create the right temperature environment in the bags so that the person sweats well. At the same time, the legs sweat just as profusely as they could when using a steam bath. It is recommended to stay in this position all night. In some cases, it may be advisable to replace the leaves around midnight if they get very wet. After undergoing several such sessions, spastic manifestations in the lower extremities will cease to bother.
Spasticity in children
Spasticity in children is the most acceptable variant of hypertonia, which passes after several stroking movements, in any case, its sharp decrease can be noted. You should not waste time when a child has a similar symptom; you should actively move the reduced limb as quickly as possible, or perform a series of passive movements. Spasticity in children can be the result of various injuries or diseases. Most often, spastic muscle contractions pursue disabled children suffering from cerebral palsy; its manifestations are also possible in case of multiple sclerosis, craniocerebral trauma and traumatic injuries of various parts of the spine. In all these cases, it is much more difficult to eliminate spasticity.
Spasticity in children is essentially an involuntary contraction of certain muscle groups. Symptoms can manifest themselves completely involuntarily, since in this situation there is no control over the energy expended by the muscles of the legs. The commands given by the brain are perceived by the muscles completely incorrectly, which causes their spontaneous contractions.
It was extremely difficult to relieve spasticity after a stroke. The point is in the emerging contradiction. We stubbornly restored strength and endurance. They did it with the help of special exercises with high load and a lot of repetitions.
For the treatment of spasticity, this is a hindrance and harm. When removing spasticity, you need a relaxing massage and light movements in exercises. In order to continue recovery from a stroke, it is necessary to conduct mutually exclusive activities. But we came up with a simple solution. Make two groups of classes.
First: to restore strength and endurance. The second to treat spasticity, restore balance and coordination. The decision turned out to be very correct. True, we didn't get to it right away and for some time did exercises to relieve spasticity along with exercises for strength and endurance. We noticed in time that the spasticity increases from active exercises.
What is spasticity
Spasticity manifests itself in stiffness. Impossible to make fast or abrupt movement. Constantly tense muscles block freedom... Feeling like you are a very rusted Terminator))).
Stress leads to early fatigue.
Stroke recovery can actually be blocked by spasticity. It is difficult to recover skills when the limbs seem to be tied with elastic bands and are always in a tense, unnatural position. To relieve spasticity after a stroke, we use elementary exercises. The main thing is to do them easily, without stress.
Muscle spasticity is an involuntary contraction, convulsions or spasm due to impaired conduction of nerve impulses after trauma to the spinal cord and brain.
Most often, this condition manifests itself at night, but it can also significantly complicate life during the day.
The mechanism of formation of spasticity
Experts call the main reason for the formation of seizures the imbalance of the inhibitory effect of the motor elements of the cerebral cortex on the cells in the structure of the spinal cord.
The natural result is the disinhibition of the tonic reflex - muscle spasticity is formed in the injured limbs of a person.
In a normal state, a person does not have to think about the sequence of phenomena produced in the muscles: which of them first need to be reduced, then relaxed - our brain has brought such an activity to automatism.
After a stroke or injury, the death of cellular elements that are responsible for special inhibitory impulses in the motor neurons of the brain and spinal cord occurs. Reflex arc: limb - spinal cord - the brain ceases to be a single system - there is a lack of coordination.
Spasms do not form immediately - for weeks, and even months. Leads to significant secondary changes in muscles and joints - enhances the negative effect of paresis on the motor system.
The severity of limb spasticity
The first signs of the onset of muscle spasticity formation are observed in the first day after injury, and subsequently tend to increase.
The degree of severity can change under the unfavorable influence of negative factors, for example:
- when the emotional mood changes - the person has a tendency to depressive states;
- when weather conditions change - fluctuations in temperature or illumination parameters;
- in case of excessive physical overload caused by the early physical activity of the victim, contrary to the recommendations of the doctor.
With an increase in the intensity of the load on the muscle fibers in the limbs, there is a difficulty in their motor activity, there are symptoms of pain in them, of varying severity.
According to the severity of spasticity, the following forms are distinguished:
Spasticity of the legs in a mild form is manifested by rapid fatigue of the muscles of the legs, a feeling of "muscle clogging", from physical activity, it becomes easier to walk on a heel, then it becomes difficult to pull the toes towards you and straighten it at the knee.
In a severe form of spasm: one or two legs are fixed in bent at the knee or hip joints, and the foot is turned inward or outward. When walking without special shoes or, deformities or contractures may occur. 
Manifestation of hand spasticity in a mild form: difficulty in extension
fingers and straightening of the arm in the elbow joint, a sign of a severe form is bent at the elbow and shoulder joints, while the hand is clenched into a fist.
If spasticity is present for a long time without treatment, contracture develops, that is, the joint is not fixed in a physiological state for the body.
In the future, the spasm will only have a negative effect on the conduct of recovery measures. In addition to limbs, it will worsen recovery in the spine: an increase in muscle tone causes pain in the back - symptoms of vertebral sciatica.
Experts note: than before adequate treatment with modern drugs was started, and also, the less the severity of spasticity, the better the prognosis of rehabilitation measures will be.
Even if the symptoms are significantly pronounced, and the treatment of seizures for certain reasons began at a later time interval - a decrease in spasticity significantly improves general well-being.
How to treat spasticity using different methods
The most important requirement for treatment is that it is as painless as possible, since the pain is exacerbated by spasticity.
An important point is the control over the activity of the pelvic organs - the prevention of inflammatory manifestations in them, as well as timely measures to prevent the occurrence of contractures, etc.
 A complex of modern treatment for getting rid of spasticity:
A complex of modern treatment for getting rid of spasticity:
- drug tactics (midocalm, baclofen);
- techniques;
- orthotics;
- surgical correction.
The complex of treatment is selected only individually, in direct proportion to the localization of the focus and the severity of spasticity. It is also necessary to take into account the technical capabilities of the medical institution.
Spasticity after a stroke or brain injury necessarily requires medication. Treatment should be carried out in stages - with a gradual increase in the therapeutic dose of medications, possibly by replacing the drug.
 Today, two subgroups are in demand:
Today, two subgroups are in demand:
- Drugs with a central mechanism of action on the negative focus - inhibition of the reflex.
- Peripheral drugs - significantly reduce the stretching reflex at the level of the spinal cord elements: muscle relaxants.
Like other subgroups of even the most modern drugs, the above ones have their own contraindications, so only a highly qualified neurologist should be engaged in their appointment.
Orthotics and plaster
Treatment of spasticity by prolonged laying of human limbs, in such a position when the muscles are optimally stretched, and tonic reflex activity is reduced, is called orthotics by specialists. It helps to reduce hypertonicity in the extremities - pathological symptoms can be reduced many times over.
In case of severe spasticity, it is even recommended to apply a special plaster splint or splint to prevent the development of contracture. It is the splint that fixes the limb in the most acceptable position - in which the muscle fibers are located in a stretched position.
Orthotics treatment is carried out from one to two hours, in direct proportion to the sensations of a person - with an increase in pain, the procedure is completed.
Physiotherapy for muscle stiffness
- local use of cold - helps to reduce excessive reflexes and maximize the range of motion, improve muscle activity;
- local use of heat - excellently contributes to a temporary decrease in tone. carried out using ozokerite or paraffin applications, the course is at least twenty procedures;
- nerve endings - an excellent technique that allows you to achieve the maximum response in the affected areas, the duration of the treatment course is prescribed by a specialist.
Exercise therapy development
 Treatment with exercises aimed at optimal relaxation of the fibers in the muscles is a long-proven, well-proven rehabilitation method for treating spasticity.
Treatment with exercises aimed at optimal relaxation of the fibers in the muscles is a long-proven, well-proven rehabilitation method for treating spasticity.
Dosed therapeutic stretching allows you to lower their tone for a couple of hours, maximize the range of motion in the affected limbs.
A kinesiotherapist knows that a decrease in tone will be observed only for a certain time and therefore it must be effectively used for other complex exercises that were difficult due to spasticity.
Surgical intervention is determined by a specialist according to strictly individual indications, when conservative techniques have already exhausted themselves, and no pronounced positive dynamics is observed.
Removing spasticity is an important task. It greatly interferes with everyday life, takes away strength and hinders movement. This makes it difficult to recover lost skills and stamina. In order to fully carry out recovery from a stroke, it is imperative to cure spasticity. We are doing this in parallel with other tasks.
With an integrated approach and the beginning of therapeutic measures at the earliest possible stage, drug treatment - the normalization of muscle tone contributes to the maximum acceleration of the patient's recovery.
In treatment, such methods as myostimulation, botox, of course, therapeutic exercises, medications (mydocalm, baclofen) and gentle surgery have shown themselves well.
What is, the causes of spasticity, prevention and treatment updated: November 21, 2017 by the author: author
