Slightly less than half of a person's body weight is in muscles. Muscle types are divided depending on the purpose, functions performed, subordination to the nervous system, and fiber structure. Without them, it is impossible to move in the surrounding space, maintain normal life processes and the constancy of the internal environment.
Musculoskeletal system
The skeleton and muscles make up the human skeleton. Bones play the role of load-bearing structures. Skeletal muscles are attached to them with connective tissues. They, unlike bones, are elastic and can deform.
Their main functions - contraction and relaxation - make it possible for a person to move in space. The skeletal muscles responsible for this process operate on the principle of levers. The passive part of the muscle (tendon) is attached to the bone at the optimal point for it to do the job. Another part of it connects to the paired part of the skeleton.
At the junction of the bones there is a joint, that is, their connection is mobile. When the muscle contracts, the force transmitted through the tendons will move the bones. 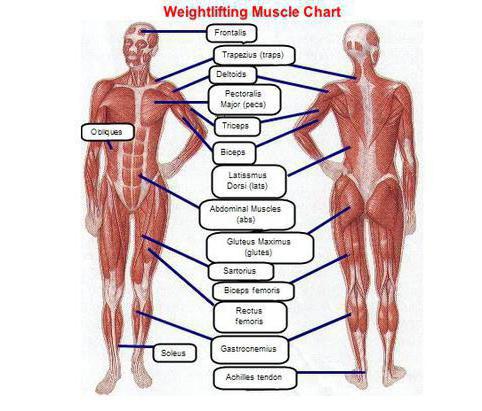
Muscular system
The human body is segmented. Muscles (types of muscles are shown in the photo above) are not located in a layer, they are divided into sections. Control is needed to work consistently. When a limb is moved, it is not just a certain muscle that contracts. At the same moment, her antagonist relaxes. In the opposite process, the functions change: the flexor relaxes, and the extensor returns to its original position.
The coordination of skeletal muscle movement is controlled by the brain. To a certain extent, this process is subject to human consciousness. And although the commands for basic movements are not given in the literal sense, they are still present in the intentions, and the brain instantly transforms them into signals that the muscles can understand.
There is another muscle system that is not completely subject to the will of a person (involuntary). This is mainly the musculature of the internal organs. The heart muscle is generally allocated in a separate group. A person does not control its contraction and does not notice it under normal conditions. The functions of the muscles of the stomach, bladder, intestines, and vascular walls are different. But their main task is to keep a specific organ in good shape and to ensure that it can perform the necessary functions. 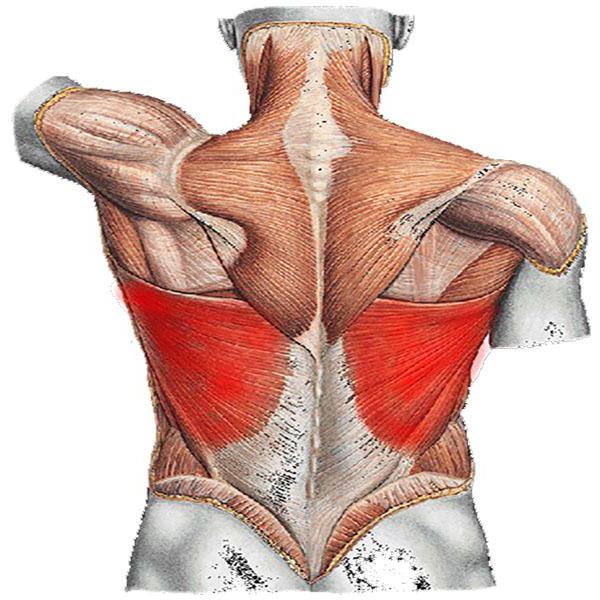
Muscles: types of muscles
The classification is made according to several factors. The main division is related to the general purpose. The musculature of the skeletal and internal organs is distinguished. Voluntarily subordinate muscles have mainly transversely directed fibers, and involuntary (internal) ones are smooth.
Depending on the localization, the muscles of the head, limbs, and trunk are divided. From what work they do, flexors and extensors are determined among them. By the type of activity among the muscles, there are synergists, that is, performing similar functions, and antagonists, acting in opposition. In shape, they can be: short and thick, long and thin. The latissimus muscles belong to the flat muscles of the back. They are responsible for pulling the shoulder towards the body and moving the arm back towards the axis of the spine.
If a muscle, during contraction, brings the limb closer to the body, then it is defined as adductor. In the opposite case, they speak of a diverting role. If a part of the body is rotated (head, forearm, shoulder), they are classified as rotational.
There is a division depending on the number of large bundles of fibers: biceps (biceps), triceps (extensor of the arm), quadriceps of the thigh. There are four components of this muscle (types of muscles: rectus, lateral, medial, intermediate). The largest is the diaphragm, the muscles of the buttocks, legs and back. The smallest is in the ear. The strongest are on the lower leg (calf) and chewing on the head. 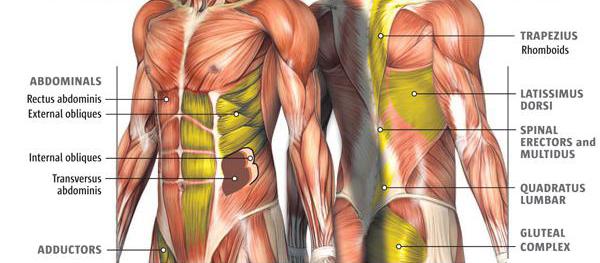
Structure
Muscle tissue in the human body is made up of cells. They have an elongated shape and are capable of contraction due to the presence of special organelles (myofilaments) in them.
There are two types of fibers: white and red. This classification is relative. But the difference can be understood in the example of chicken meat (breast and drumstick). The first is white. The chicken chest does not work as often as the shins. She rarely flaps her wings, but they are capable of a sharp burst of activity, making it possible to rise into the air.
On the other hand, your whole life goes on on your feet. Their tissues can work for a long time, but they are not capable of such a sharp surge in activity. in chickens, they are densely permeated with a network of capillaries (hence the color), since they need more nutrition (constant and sufficient) to maintain tone.
Musculature is arranged according to a similar principle in humans. There is evidence that the average person has white tissue and red tissue in a ratio of 4/6. For sprinter athletes, the picture is different. Their fast white muscles are superior. This is partly achieved by training, but not every person is able to transform so much. 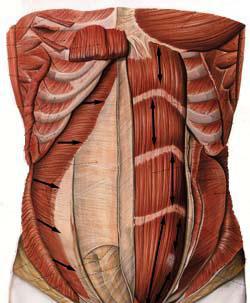
Fiber bundles
Skeletal muscles are characterized by the speed of contractions. Their tissue cells are relatively large, elongated and multinucleated (up to 100 or more). If viewed under a microscope, the section looks like it is lined with alternating stripes of light and dark colors (cross-striped). Smooth muscle tissue consists of mononuclear cells. They are more uniform and less elongated.
Skeletal muscles are assembled from bundles of the first (thinnest), second (larger), etc. order. From the method of placement in relation to the axis of the spine, rectilinear muscles (rectus abdominis muscle), oblique (abdomen: internal and external) and transverse (directed perpendicular to the vertical axis - the transverse muscle of the chest) are separated.
Depending on the location around the tendons, they are divided into parallel (spinous) and circular (mouth, rectal sphincter, vagina).
The heart muscle tissue is special. It consists of binucleated cells (cardiomyocytes). They are intertwined, so that they grow together with each other, connecting with the cytoplasm. A feature of the heart muscles is the ability to work rhythmically and constantly. 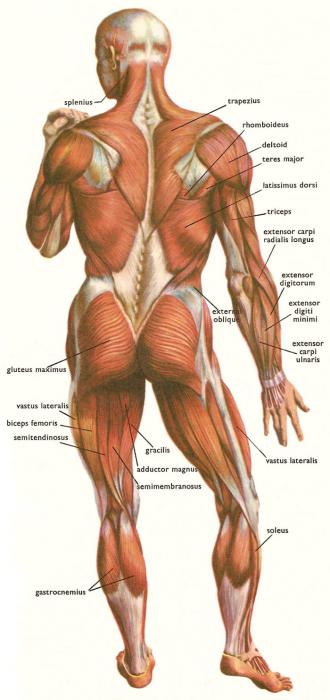
Work
Even with a seemingly calm state, the muscles are still ready for immediate contraction. This condition is called tone. Nerve impulses are constantly being sent to all organs from the brain. In a relaxed state, the number decreases, but there are enough of them to exchange information. Without this control, there would be no way to keep the body balanced and stable.
The energy source for working muscles is adenosine triphosphoric acid (ATP). It is formed as a result of a complex cycle of glycogen breakdown. Cell nutrition is carried out with blood flow. From this it follows that all major muscles should be densely braided with capillaries, arteries and veins.
They are not able to work constantly, they need rest. If this is neglected, then the efficiency decreases, which is manifested by a violation of the conduction of impulses and the response to nervous excitement. Under intense loads, metabolic products accumulate, which prevents an even distribution of impulses.
Localization
The human body is built on the principle of bilateral symmetry, so all the main muscles are paired or consist of two halves. Those located on the head participate in mimic contractions, which make it possible to express emotions (joy, grief, fear, pleasure). Another important function is the work of the oral apparatus (chewing, swallowing). They also provide the eyes (movement of the eyeballs, blinking of the eyelids).
On the neck, the musculature raises and lowers the head, turns it and supports it in the axis of the spinal column. On the torso, a distinction is made between the front and the back. Divided into the upper section (the work of the shoulder girdle); chest (breathing); abdominal (abdominal tone). The largest part of the back is covered by the latissimus muscles. In addition to participating in the extension of the arms and circular movements of the shoulders, they form behind, below the ribs, a body frame, covering the kidneys and liver. They are active during swimming, work with a deep breath, raising the lower ribs.
In front, in the upper part, in the area of coverage, the pectoralis major muscles are in the lead. In the abdomen, this is a deep and thin transverse muscle. It is she who resists gravity and maintains the constancy of the environment of the internal abdominal cavity. Together with the press, it provides a flatness of the abdomen.
At the junction of the trunk and lower extremities, an important place is occupied (large, medium, small). On the thigh can be distinguished semi-membranous, biceps, short, long and large adductor. On the lower leg - gastrocnemius, soleus. And on the foot - flexors and extensors of the fingers. 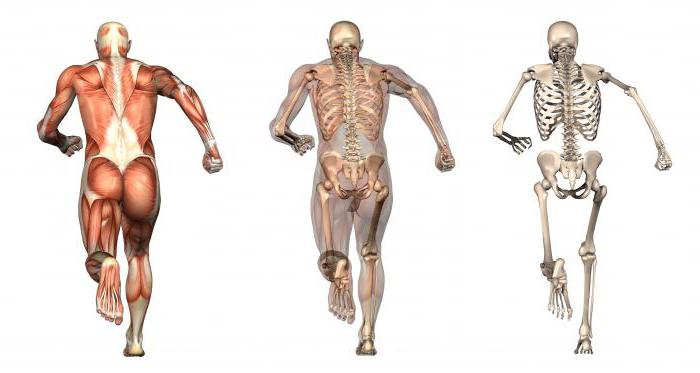
Role for the body
Without proper activity, a person's muscles can atrophy. It has been noticed that at minimal loads, the cells are renewed every one to two weeks. This happens more often when playing sports. The growth of muscle tissue during loads with additional weight occurs due to the fact that a part is torn. The body seeks to recover, new cells grow, connections are renewed. This is accompanied by an increase in their volume and mass.
In addition to the implementation of cardiac activity, maintaining the shape of the body, ensuring an upright position and movement, the muscles make possible a number of other equally important processes: speech (larynx and tongue), breathing (diaphragm), digestion (esophagus, stomach tone, intestines). The excretion of metabolic products (bladder, rectal sphincter) is also ensured.
If a person does not have the ability to control the activity of the involuntary muscles, then the voluntary (main muscles) can even train. Well, a healthy lifestyle and keeping the body in good physical shape, as you know, is the key to well-being and peace of mind.
Now you know what role muscles play in the body. Muscle types differ in their structure and function.
