The human body is an amazing system that surpasses many man-made constructions in its complexity. Despite this, the person acts remarkably well-coordinated and accurately, effectively fulfills the assigned tasks. The movement of the body is carried out with the help of muscles, which are located almost throughout its entire area. Thanks to their selfless work, we can walk, breathe, speak and do other things that are so familiar to us.
Muscle types
The name of human muscles came to us from ancient Rome, whose inhabitants compared the movement of muscle tissue under the skin to the running of mice under a sheet. Thus, for fun, the Romans called muscles by the Latin word musculus, which translates as mouse. The comparison turned out to be so successful that the word is still used to this day. The "little mice" perform their work thanks to their ability to contract. attached by tendons to the periosteum, the connective layer of the skin, or to another muscle.
Tendons are built from dense connective tissue. They are extremely durable and can withstand severe stress. Muscle tissue contains nerves, which carry signals from the spinal cord, and blood vessels, which provide this entire complex system with fuel. Depending on the structure, smooth muscles are distinguished, striated, as well as cardiac muscle, or myocardium.
Smooth muscles
This type of muscle tissue is not visible to the eye, as, for example, human skeletal muscle. The diagram from the anatomical atlas also dispenses with them. Smooth muscles form the walls of hollow internal organs such as the bladder, intestines, stomach and genitals. Also, this type of muscle tissue forms the vessels through which blood and lymph move.
Unlike skeletal muscles, smooth muscles do not obey our will. This ensures the uninterrupted operation of the most important systems of the body, interference with which could lead to negative consequences. Smooth is very plastic - it stretches well and can remain in this form for a long time without losing tension. This type of muscle contracts slowly, which is perfect for the responsibilities that are assigned to it.
Striated muscles
The muscles in which our skeleton is clothed are called striated. This most noticeable pattern of their arrangement allows our body to perform the full range of movements that we are accustomed to. The mass of these muscles is about 40% of the total body weight in men and 30% in women. Each muscle is attached to the skeleton so that when it contracts, movement occurs in one of the joints. The layout of human muscles resembles a mechanism that moves the body through a system of blocks and levers.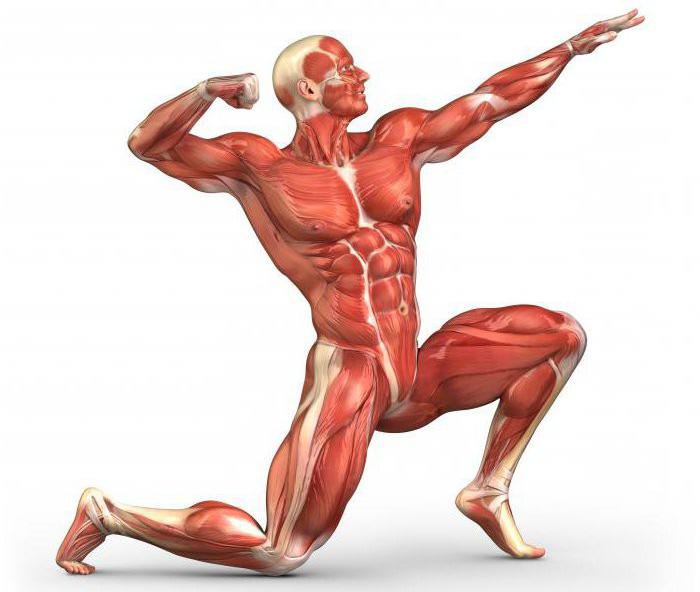 
Depending on the work being done, muscles can be synergistic or antagonistic. The synergists work together to accomplish the task at hand, while the antagonists do the opposite. That is, when a muscle contracts, its antagonist must relax for movement to occur. The easiest way to understand this principle is with the example of biceps and triceps. If you need to bend your arm, then the biceps muscle strains, and the triceps muscle relaxes. The opposite process is required to extend the arm. However, this does not always happen, for example, in order to keep the load on an outstretched arm, we need to use both biceps and triceps. In this case, they will act as synergistic muscles.
Muscle contraction does not always happen with tension. If only the length of the muscle changes, then this mode of operation is called isotonic. If muscle tension occurs, and its length remains the same, then such a load is called isometric. 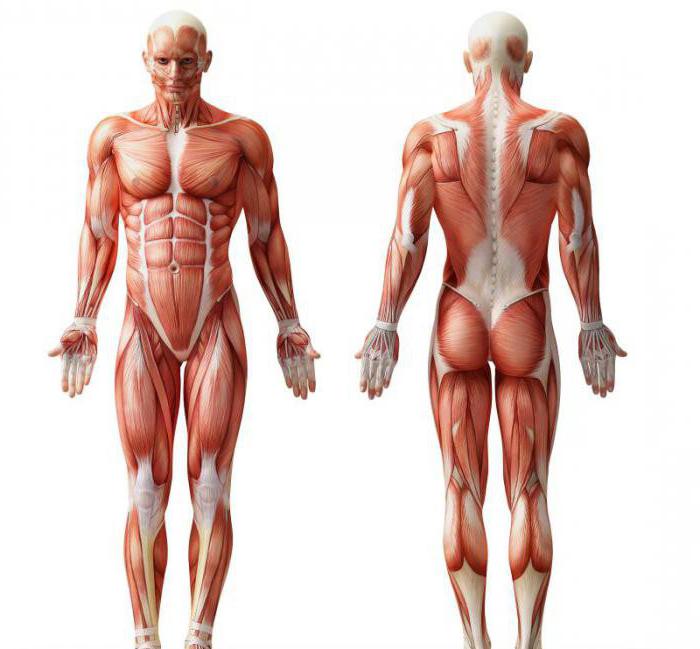
Another interesting muscle is the heart. It is not for nothing that it is called the main engine of our body. Its continuous work ensures the vital activity of a person, driving out liters of blood inside him. This organ consists of striated muscle tissue, which, in contrast to the skeletal, collected in bundles, is intertwined in some places. This structure allows the heart to contract quickly. Unlike skeletal muscles, the myocardium does not obey our commands, but works autonomously.
Nervous system
Inside each muscle are the highways of nerves and blood vessels. Of course, it is the brain that is the starting point of the nerve impulse, but without the spinal cord there would be no way to competently organize the muscles of a person. The pattern of future movement is formed precisely in the bowels of the spinal cord, from where an ordered signal enters the muscle. Thanks to this, the muscles work in concert, for example, when a muscle is excited, its antagonist is inhibited. At the same time, if necessary, both of them can be excited if the desired signal is generated. 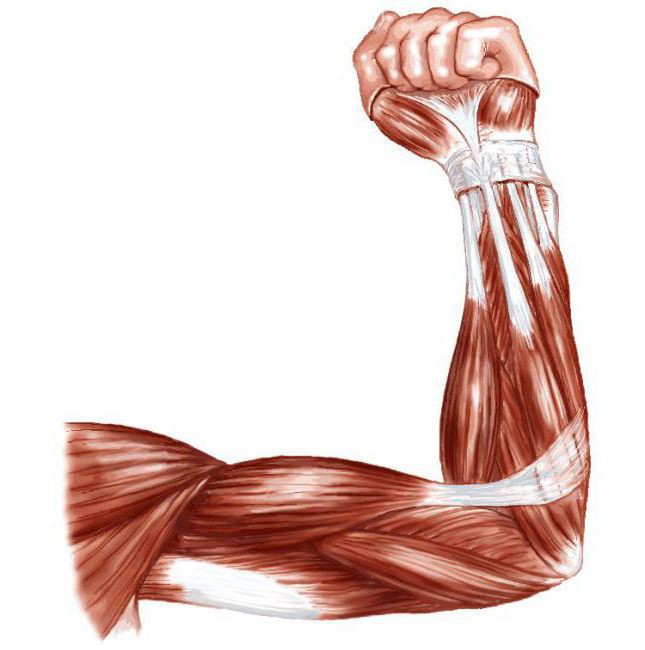
Feedback occurs along the nerve fiber, thanks to which the brain knows what state the muscle is in. This complex system is controlled by motor neurons, which receive signals in two ways. One of them is for conscious actions, the other is for reflex and automatic actions, such as walking, breathing or running.
Human muscle groups
Muscles can be divided into separate groups, each of which has its own characteristics. The human scheme assumes their conditional division into:
Four-headed.
Three-headed.
Calf.
Trapezoidal.
Abdominal muscles.
Flexors of the arms.
Arm extensions.
Buttock.
Leading muscles.
Wrist flexors.
Wrist extensors.
Blade clamps.
Sciatic-tibial muscles.
Lumbar.
These groups include the main muscles of a person, the layout of which is partially displayed in these groups.
Muscles and man
Muscle work is very important for health, keeping them in good shape is the key to a long and active life. Unfortunately, many people know about this, actively discuss the role of sports in the formation of good health, but continue to lead a sedentary lifestyle. Thus, entire muscle groups of a person remain unused. ![]() A sedentary lifestyle causes muscle tissue atrophy, diseases of the cardiovascular system. The pampered heart can no longer bear even minor loads, as well as the lungs, the volume of which inevitably decreases. Remember, it is impossible to stay healthy if your muscles are constantly inactive. Give them a job - and the result will not be long in coming.
A sedentary lifestyle causes muscle tissue atrophy, diseases of the cardiovascular system. The pampered heart can no longer bear even minor loads, as well as the lungs, the volume of which inevitably decreases. Remember, it is impossible to stay healthy if your muscles are constantly inactive. Give them a job - and the result will not be long in coming.
